Multiscale Studies on the Transport Behavior of Nitrogen Foam for Improving Oil Recovery in Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Carbonate Reservoirs
本研究系统评估了氮气泡沫在碳酸盐油藏中的提高采收率(EOR)潜力,实验与数值模拟相结合,覆盖从岩心尺度到油田尺度的多尺度研究。研究采用印第安纳石灰岩岩心,在55°C、高盐度(11万ppm)条件下进行泡沫驱实验,考察泡沫质量、注入速度、表面活性剂浓度和渗透率对泡沫强度与驱油效率的影响。
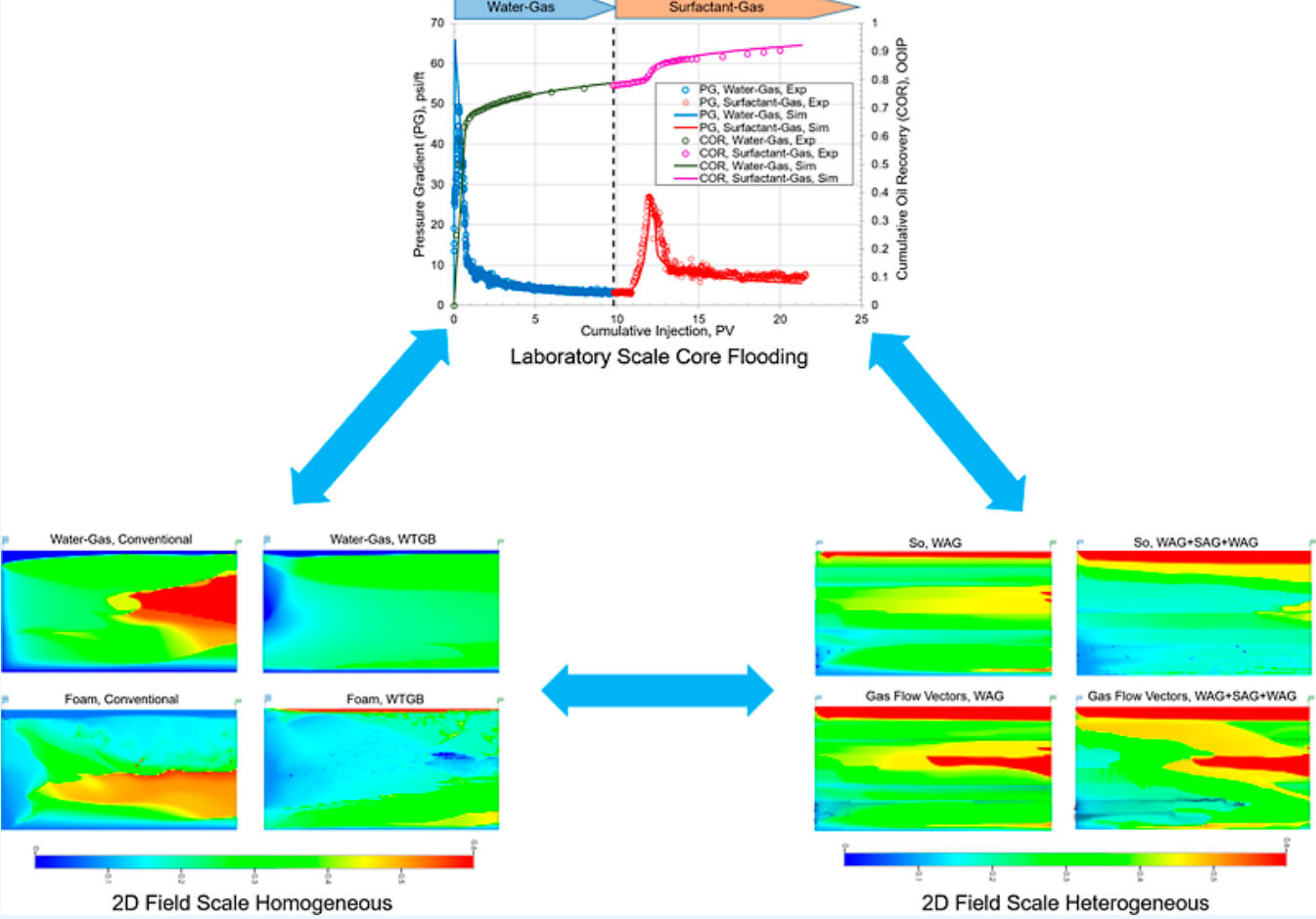
在实验基础上,利用CMG-STARS模拟器建立一维与二维模型,结合历史拟合方法提取泡沫运移的关键参数(如干燥效应、剪切变稀行为、油相失稳效应等)。研究进一步提出“水上气下”(WTGB)注入策略,有效缓解重力分异问题,并通过WAG(水气交替)与SAG(表面活性剂-气体交替)注入方式提升泡沫波及效率。
研究结果表明,泡沫可显著提高碳酸盐油藏中的原油采收率,尤其适用于油湿、非均质性强的油藏条件。
CMG软件应用情况
本研究广泛使用 CMG-STARS 模拟器进行泡沫驱建模与数值模拟,主要应用包括:
- 构建一维岩心尺度的泡沫驱模型,用于历史拟合提取泡沫参数;
- 建立二维均质与非均质油藏模型,模拟不同注入策略下的泡沫运移行为;
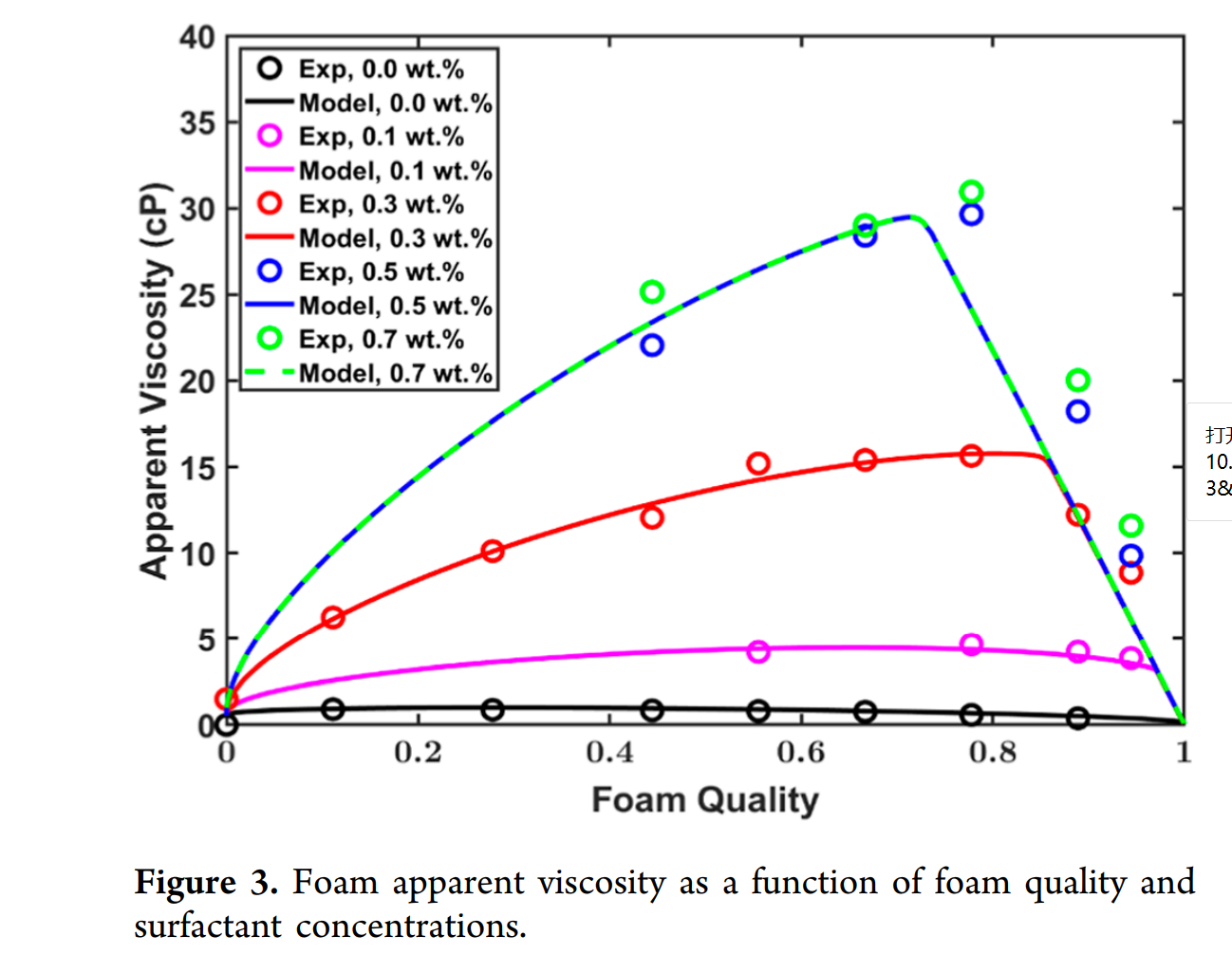
- 使用STARS局部平衡泡沫模型,考虑泡沫干燥效应、剪切变稀、油相失稳、表面活性剂浓度等影响因素;
- 利用CMOST辅助历史拟合,优化泡沫模型参数(如FMMOB、FMDRY、FMOIL等);
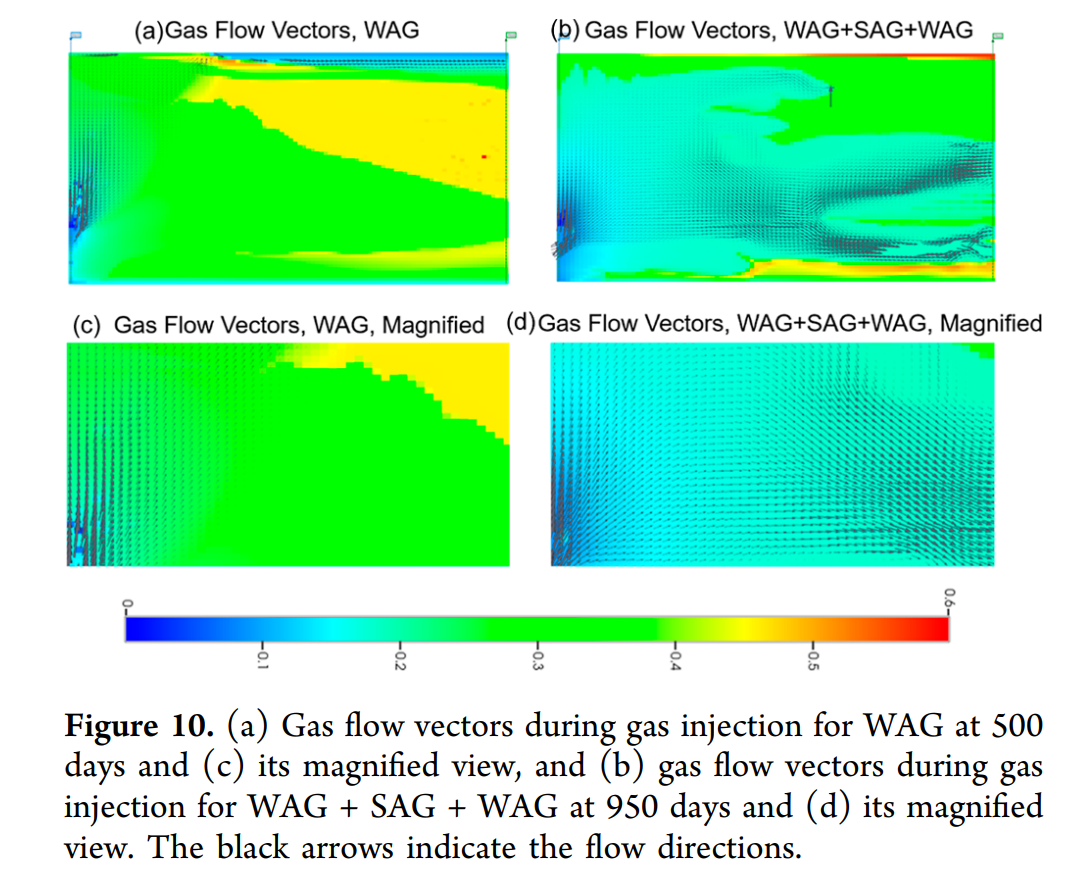
- 模拟不同注入方式(WAG、SAG、WTGB)下的泡沫驱动态与采收率变化。
研究结论
- 泡沫驱显著提升采收率:在岩心尺度实验中,注入2.5 PV氮气+0.3 wt.% APG表面活性剂泡沫(70%泡沫质量)可回收超过8% OOIP的残余油。
- WTGB注入策略有效缓解重力分异:通过“水上气下”注入方式,利用浮力与重力差异,显著改善泡沫与气体的垂向分布,提高波及效率。
- 表面活性剂浓度对泡沫性能影响显著:提高SAG段塞中的表面活性剂浓度可增强泡沫稳定性与驱油效率,推荐浓度为0.3–0.5 wt.%。
- 泡沫在非均质油藏中表现优异:泡沫可显著降低高渗层气体流度,改善低渗层波及效果,有效提升非均质油藏的整体采收率。
- 泡沫模型参数可通过实验与拟合有效获取:通过CMG-STARS模拟器与实验数据的历史拟合,可准确建立适用于油田尺度的泡沫模型。
作者单位
中国石油勘探开发研究院
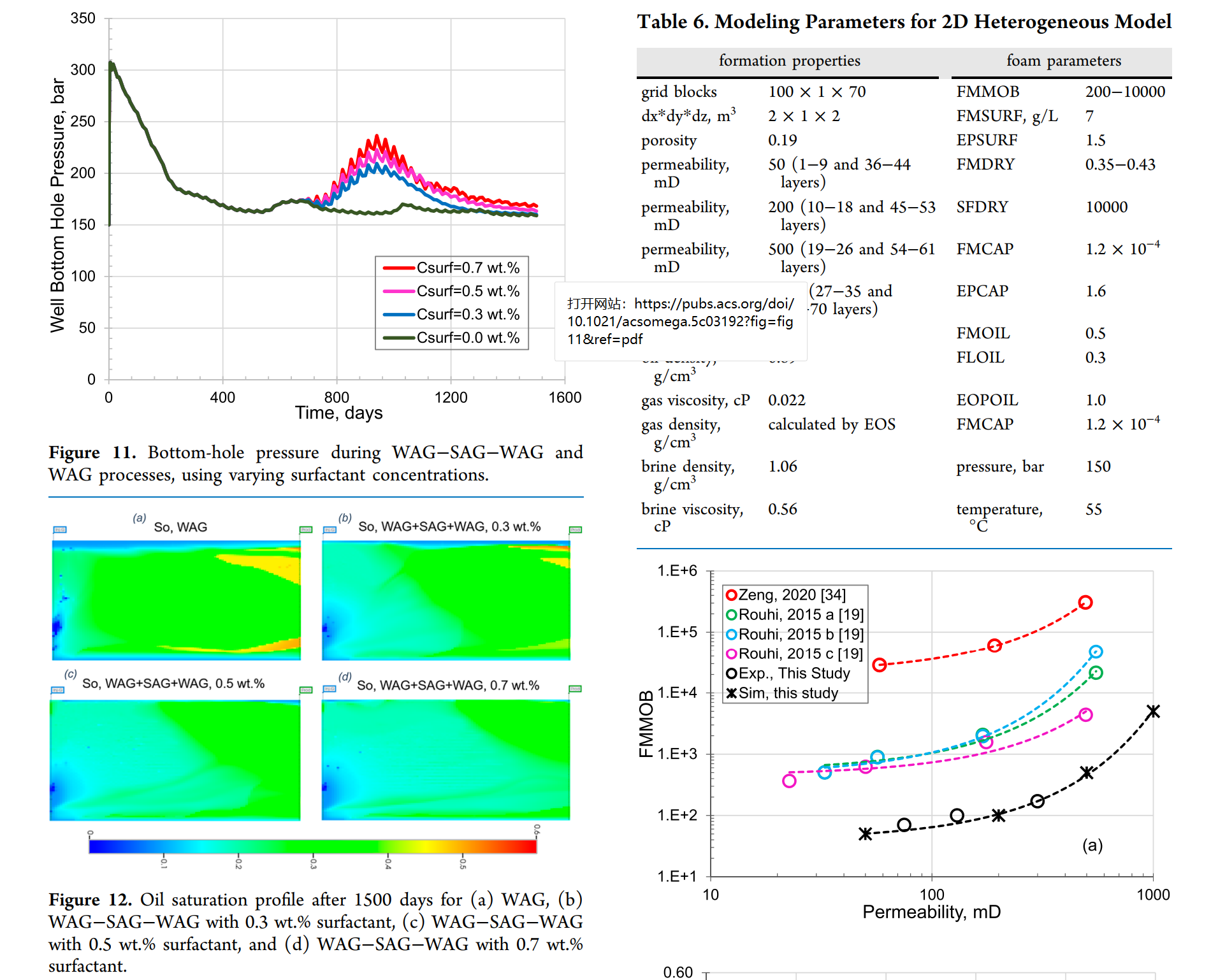
ABSTRACT:
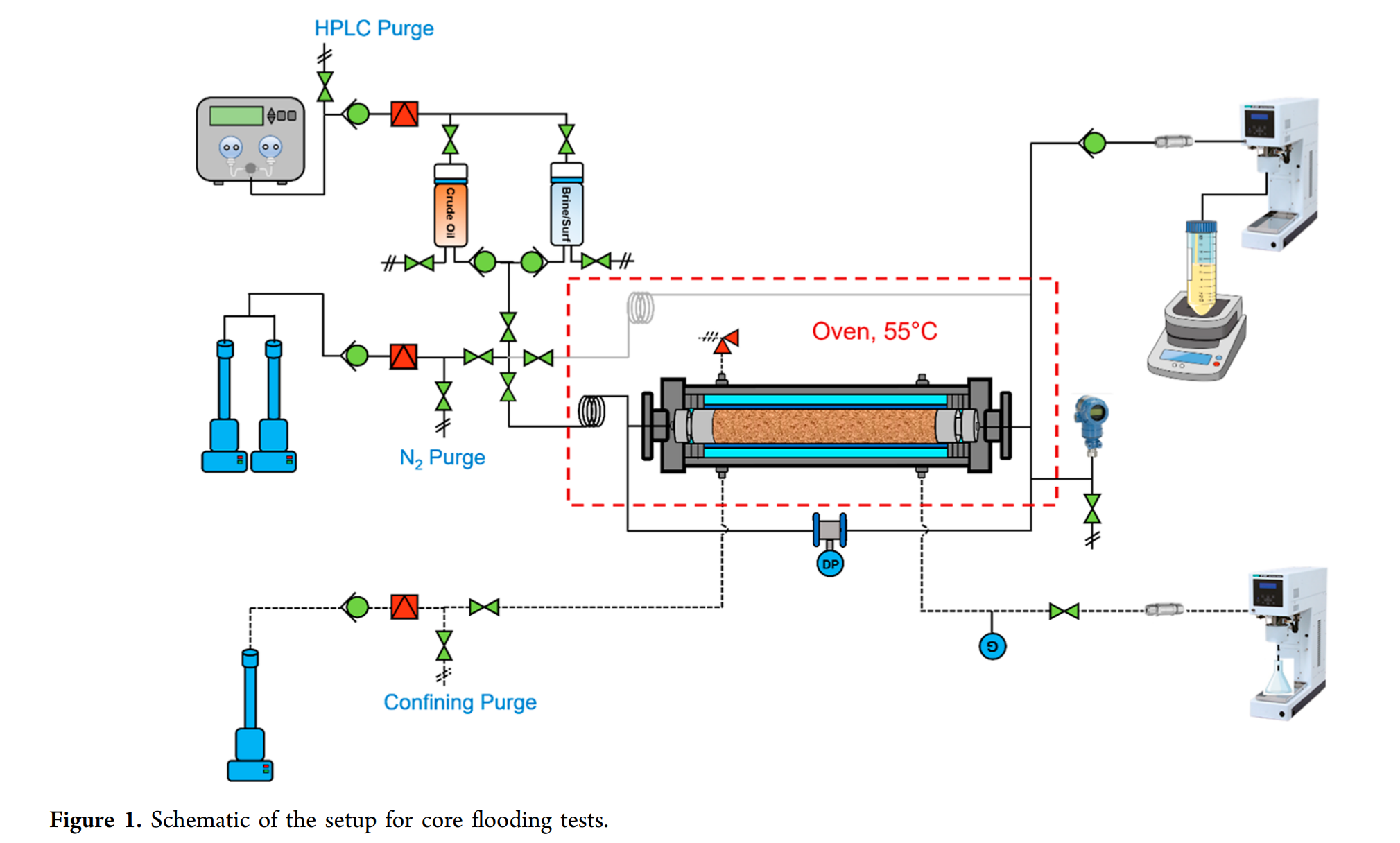
This paper presents the viability of utilizing foam to enhance oil recovery in carbonate reservoirs, characterized by medium temperatures (55 °C) and formation salinity. The foam tests first examined the effects of foam quality, injection velocity, surfactant concentration, and permeability on foam strength and incremental oil recovery on Indiana Limestone on a laboratory scale. Over 8% of the water−gas-flooded residual oil was extracted following the coinjection of a 2.5 total pore volume of nitrogen and 0.3 wt % APG surfactant (in synthetic formation brine) at a foam quality of 70% (4 ft./d). The modeling parameters for the foam dry-out effect, surfactant-dependent function, flow rate-dependent function, and oil destabilization effect were derived from history matching of gas/surfactant coinjection tests conducted at different foam qualities, surfactant concentrations, and injection rates. The viability of foam for EOR is evaluated by using two-dimensional synthetic homogeneous and heterogeneous models at the field scale. Enhancing the surfactant concentration in the surfactant-alternating-gas (SAG) slugs can significantly improve the foam efficiency, effectively redirecting gas injection into unswept regions. The numerical modeling results indicate that the APG foam possesses significant potential to improve oil recovery in both homogeneous and heterogeneous oil-wet carbonate reservoirs. It is also found that the water-top-gas-bottom (WTGB) injection strategy can successfully alleviate gravity segregation in a multizone completion wellbore by leveraging the buoyant force of the gas and the gravitational force of the aqueous phase.
