Multiobjective optimization of CO2 injection under geomechanical risk in high water cut oil reservoirs using artificial intelligence approaches
我国东部大庆、胜利等高含水老油田水驱后含水普遍超过90%,常规手段提高采收率已十分困难;CO₂驱可在水驱基础上再增油10–20%,同时实现CO₂封存。但CO₂注入会改变孔隙压力,诱发断层滑移和微地震,现有研究多忽略地应力风险。本文构建“CMG-GEM流-固耦合数值模拟+机器学习代理模型+多目标优化”一体化框架,以“最大油田采收率(FOR)+最大CO₂封存率(CSR)+最小断层滑移位移(FSD)”为三重目标,针对含水70 %、80 %、90 %三种工况,采用拉丁超立方采样(LHS)生成4000组注采方案,训练LSTM与Gaussian-SVR代理模型,并用NSGA-II、MOPSO算法求取Pareto前沿。结果表明:LSTM代理模型整体优于Gaussian-SVR;NSGA-II收敛更快、结果更可靠;随含水上升,最优平均注气量降低、产液量升高;含水≥90 %时FSD代理模型误差超±20 %,建议现场控制含水<90 %。
CMG软件应用情况
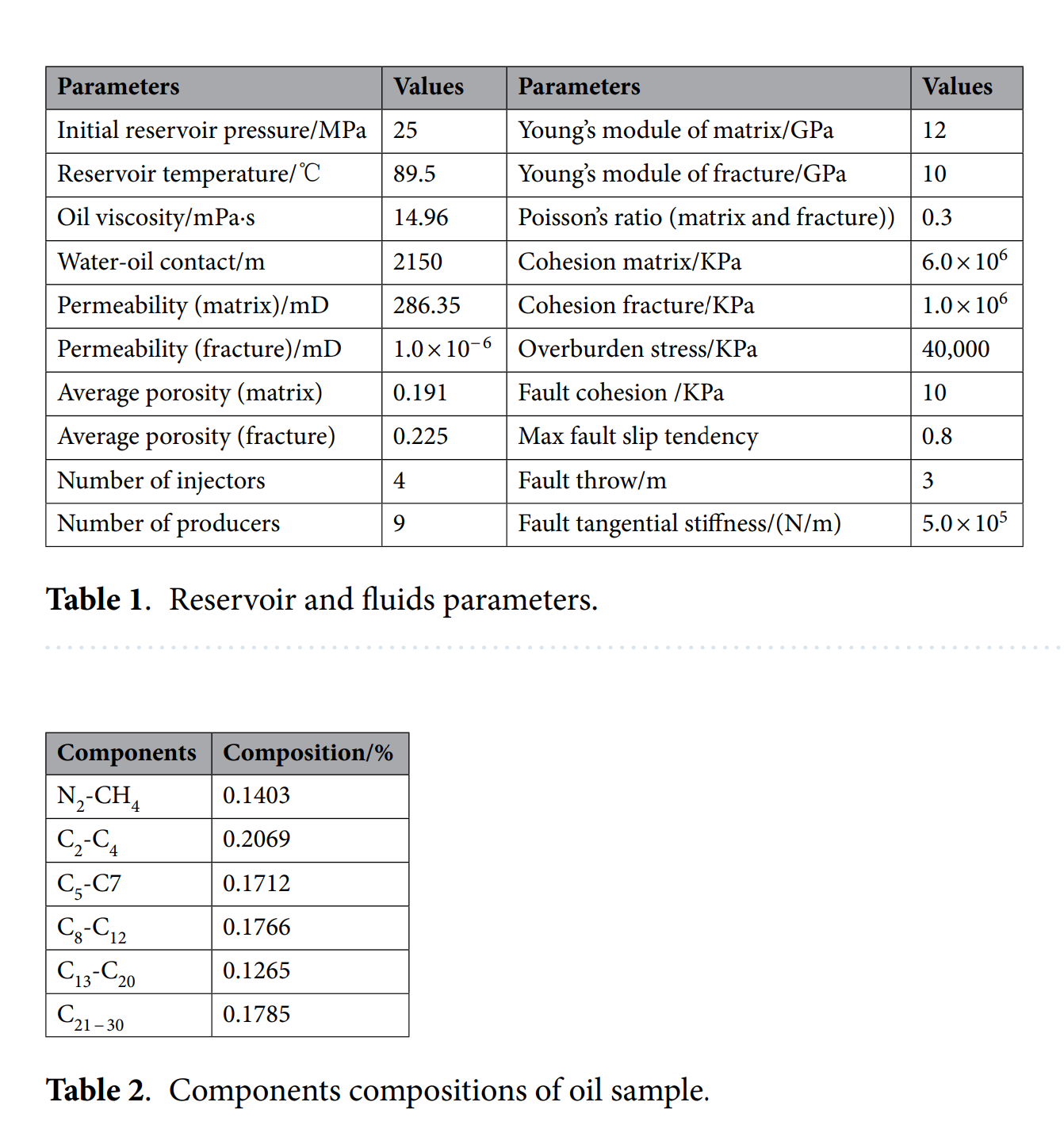
• 模块:CMG-GEM(组分、双孔双渗、流-固耦合)
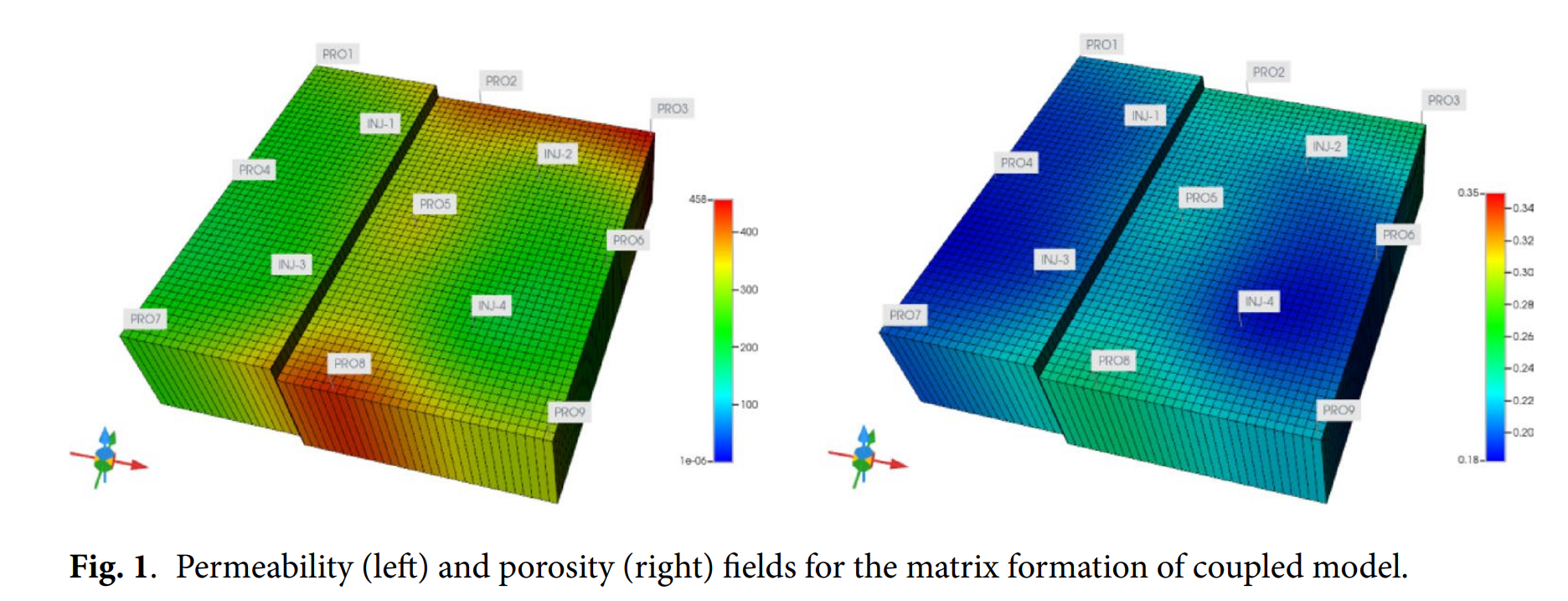
• 模型:52×49×1=2548网格,五点井网(4注9采),断层贯穿储层
• 耦合方式:GEM流体压力→地应力场→断层滑移→渗透率/孔隙度动态更新
• 计算量:单算例1.5 min,4000算例并行,总耗时≈1天
结论
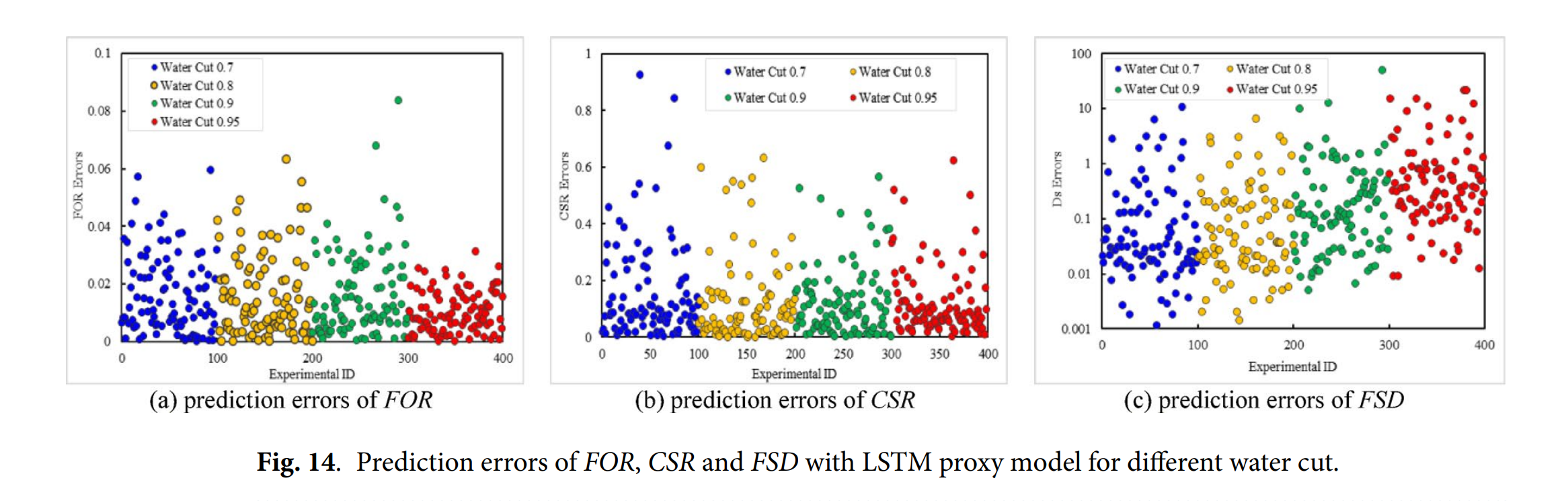
- 机器学习:LSTM对FOR、CSR、FSD的预测精度均高于Gaussian-SVR,但含水>90 %时FSD误差>±20 %。
- 优化算法:NSGA-II在收敛速度、Pareto前沿质量上优于MOPSO。
- 参数规律:随含水升高,最优注气量由51×10⁴ m³/d降至40×10⁴ m³/d,产液量由557 m³/d升至590 m³/d;FOR稳定在42–45 %,CSR由0.78升至0.94,FSD由9.7 mm降至0.2 mm。
- 工程建议:高含水油田CO₂驱应同步优化注气-产液制度并实施断层实时监测,含水控制在90 %以下可兼顾增油、封存与安全。
Abstract
To obtain the maximum field oil recovery (FOR) and CO2 sequestration ratio (CSR), it is imperative to optimize the CO2 injection and liquid production rate. However, previous studies ignore the geomechanical risks indeed. Therefore, a hybrid optimization framework was designed that combines artificial intelligence methods (Support Vector Regression with the Gaussian kernel, Gaussian-SVR or Long Short-Term Memory, LSTM) and multi-objective optimization algorithms (multiple objective particle swarm optimization, MOPSO or Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II, NSGA-II) to find the optimal CO2 injection and production strategies under different water cut. With this framework, the largest oil recovery and CO2 storage under the lowest fault slip displacement (FSD) can be obtained simultaneously. In this framework, Latin hypercube sampling (LHS) is used to produce the samples for training and testing for cases with water cut 0.7, 0.8, 0.9 and 0.95, and the corresponding results are obtained from numerical simulations. Thus, Gaussian-SVR and LSTM are trained as the proxy model to substitute the numerical simulator. Thus, the MOPSO and NSGA-II are utilized to determine the Pareto Front of the optimum result and work schedules. A synthetic case reservoir model with high-water cut and one fault is employed to test the robustness of this framework. The results show that compared with FOR and CSR, due to the serious nonlinearity, the training and prediction of FSD with the proxy model are not very good. The prediction errors increase with the water cut, and when the field water cut is larger than 0.9, the practical requirements (± 20% errors) are not yet met. In general, the performance of proxy model with LSTM is superior to the Gaussian-SVR. The solutions obtained from the Pareto optimal set for the NSGA-II algorithm exhibit faster convergence, better superiority and reliability than MOPSO. As the rise of water cut, the optimal average field gas injection rate (FGIR) decreases, while the average field liquid production rate (FLPR) increases. The novelty of this work mainly lies in the consideration of fault slip during CO2 injection for multi-objective optimization in high-water cut oil reservoirs, which can provide some guidance for the design of schemes.
