Preventing Salt Precipitation in CO2 Storage Processes in Saline Aquifers: Dissolved-Water CO2 Injection Method
CO₂在地质构造中的储存,尤其是深部盐水含水层中的储存,是碳捕获和储存技术的关键组成部分,对于缓解温室气体排放具有重要意义。然而,这些含水层的高盐度带来了盐析的风险,导致压力升高和注入能力降低。开发一种防止盐析的方法仍然是一个挑战,本研究聚焦于此。提出了水溶CO₂注入(dwCO₂注入)作为一种防止盐析的新方法,即在将CO₂注入含水层之前先使其与水混合。通过CMG-GEM模拟器在碳酸盐含水层中检验了六种不同情景,结果表明,使CO₂饱和水可以将盐析减少到几乎为零,而溶解2000 ppmv的水可以使盐析减少到三分之一。需要指出的是,注入湿CO₂需要特殊的方法来应对潜在的挑战,包括腐蚀和水合物形成的风险,论文也对此进行了讨论。
CMG软件应用情况
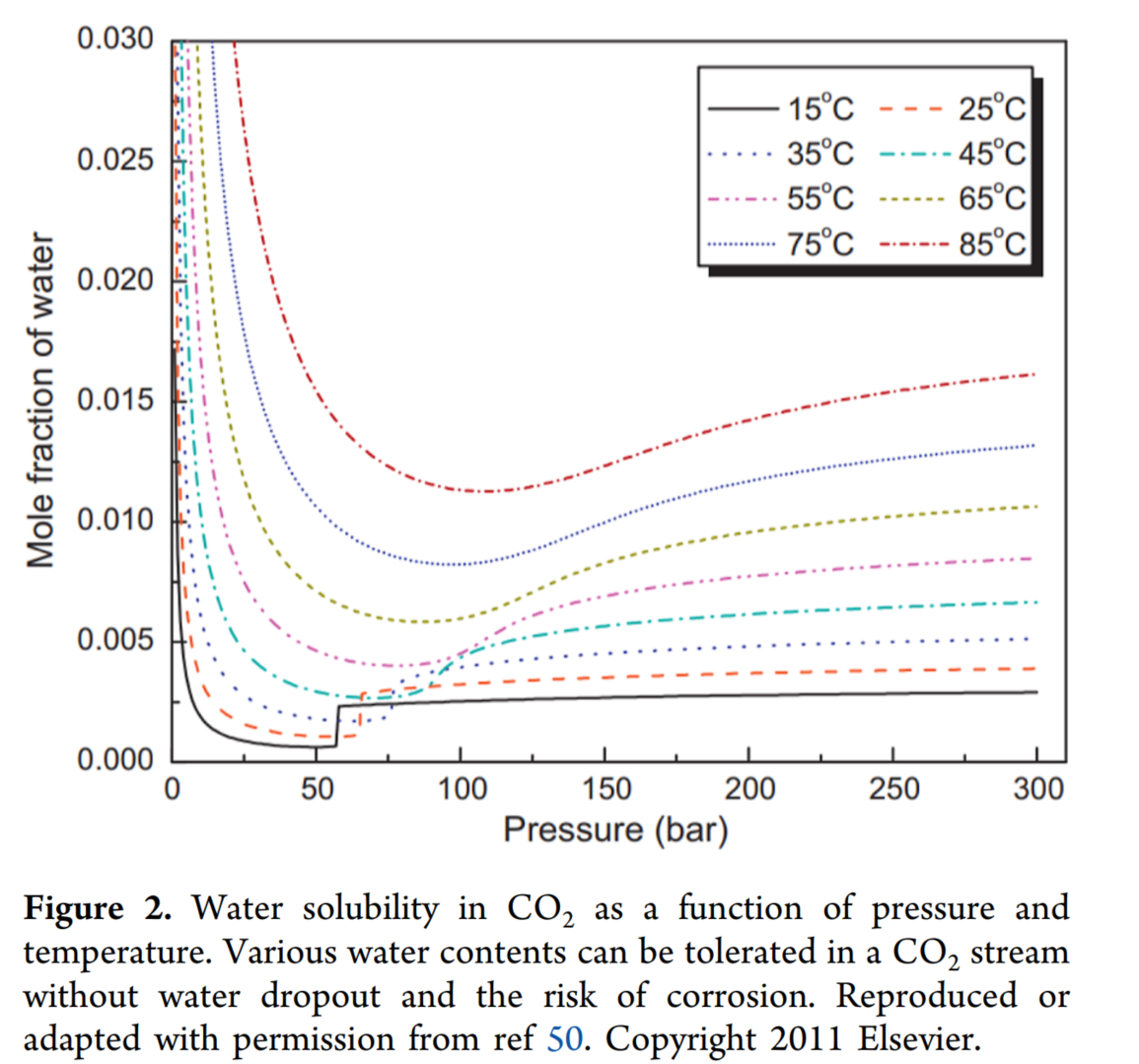
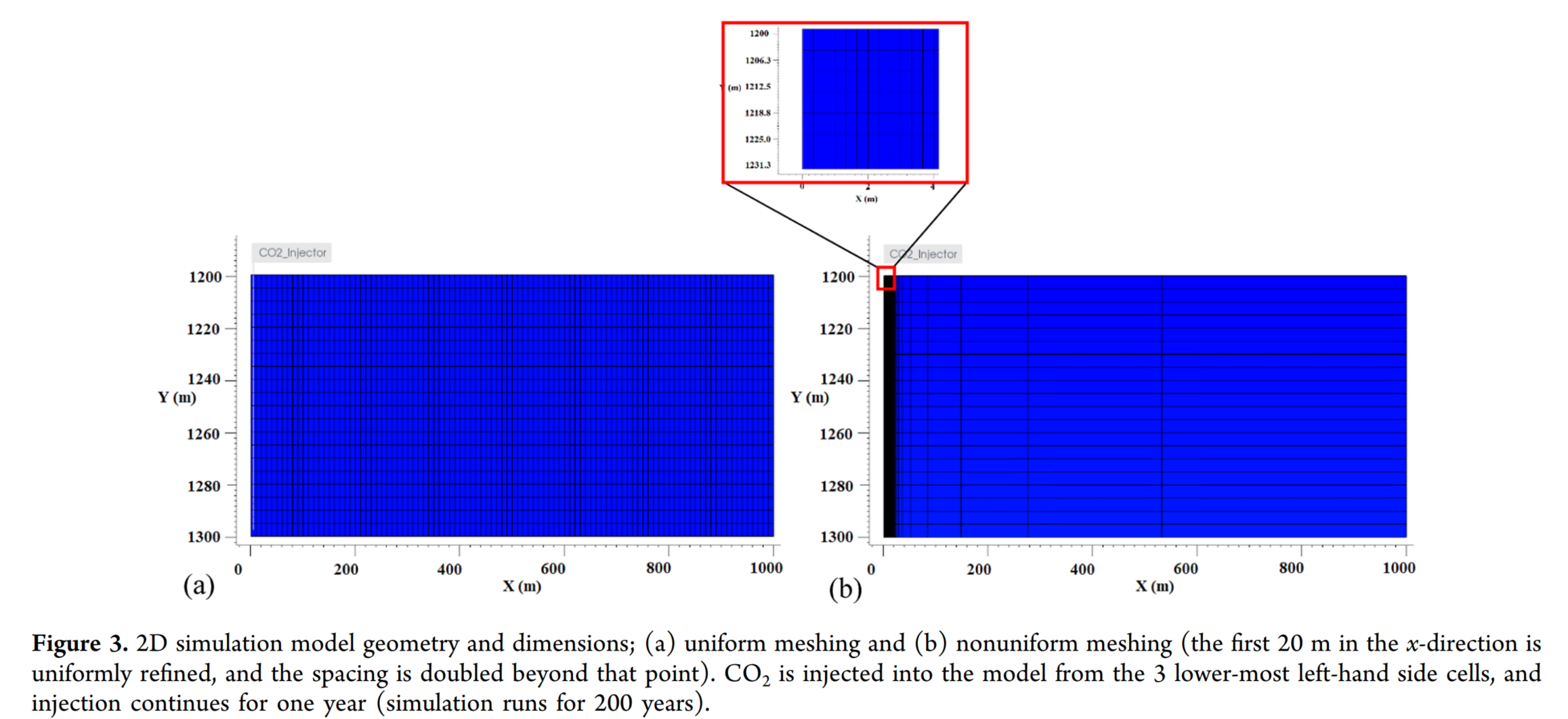
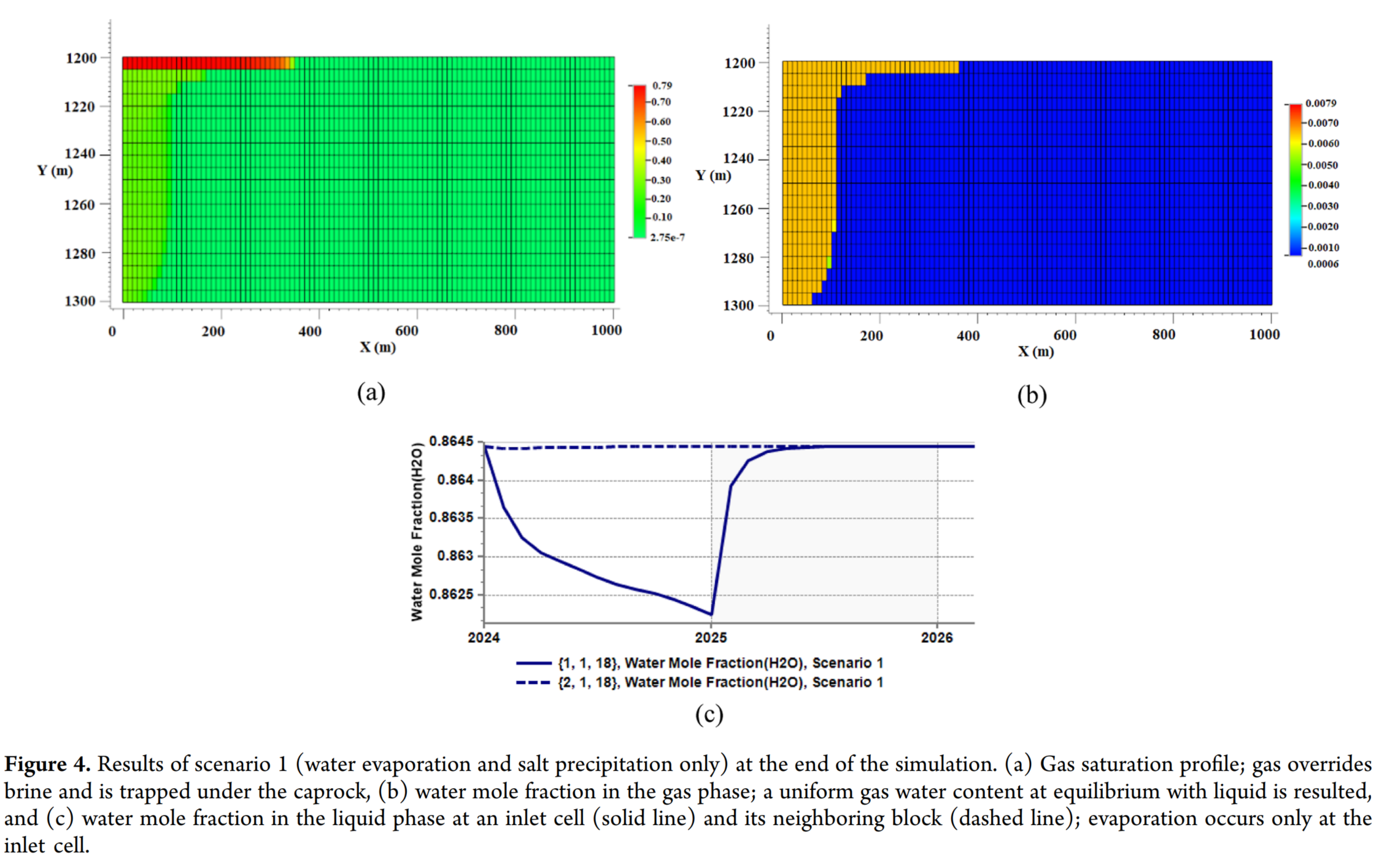
本研究使用了CMG(Computer Modeling Group Ltd.)的GEM组分模拟器来模拟CO₂在碳酸盐含水层中的储存过程。通过构建一个二维矩形含水层模型(尺寸为1000 m × 100 m),并设计了六种不同的模拟情景,来研究水蒸发、盐析、CO₂溶解、地质化学反应以及毛细效应等现象及其相互作用。模型假设了一个碳酸盐岩储层,完全被盐水饱和,并且在注入井附近有三个最低的网格被射孔,用于向含水层中注入CO₂。模拟运行了200年,以观察CO₂羽流的演变及其与地下环境的相互作用。通过这些模拟,研究了不同情景下的盐析、孔隙度变化以及CO₂的捕获和储存效率。
结论
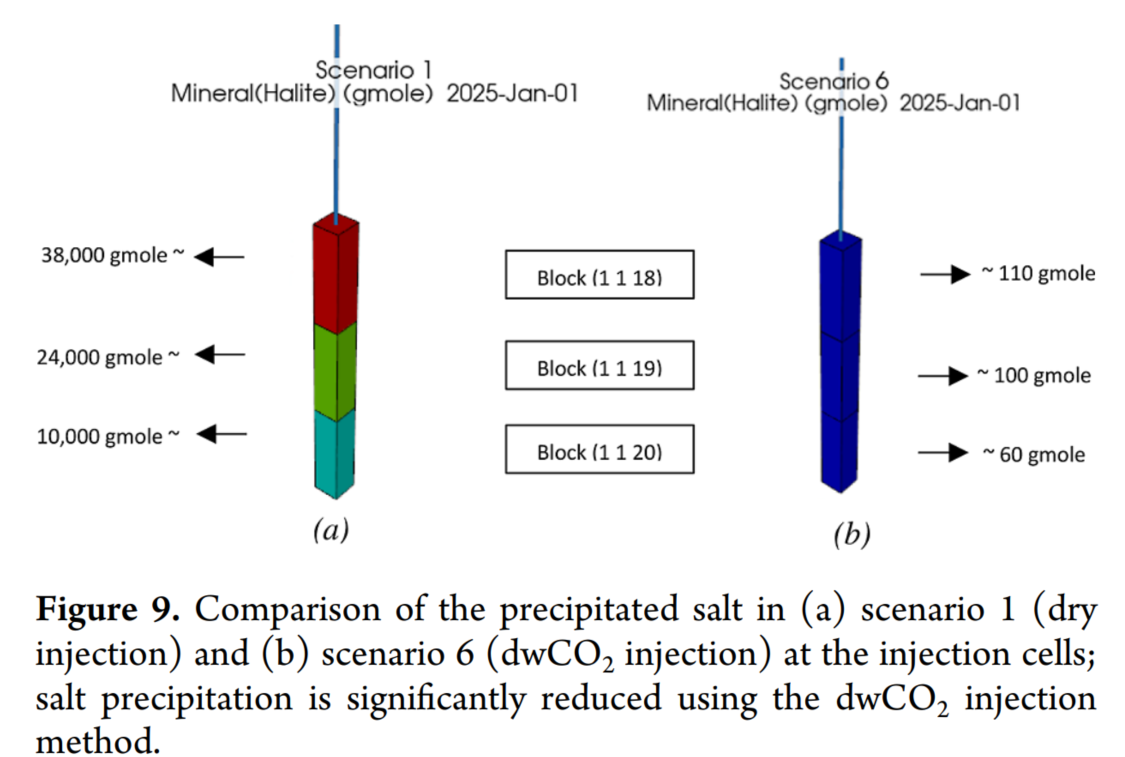
- 通过模拟研究发现,使CO₂饱和水可以显著减少盐析,几乎将其降低到零。
- 在注入的CO₂中溶解2000 ppmv的水可以使盐析减少到三分之一。
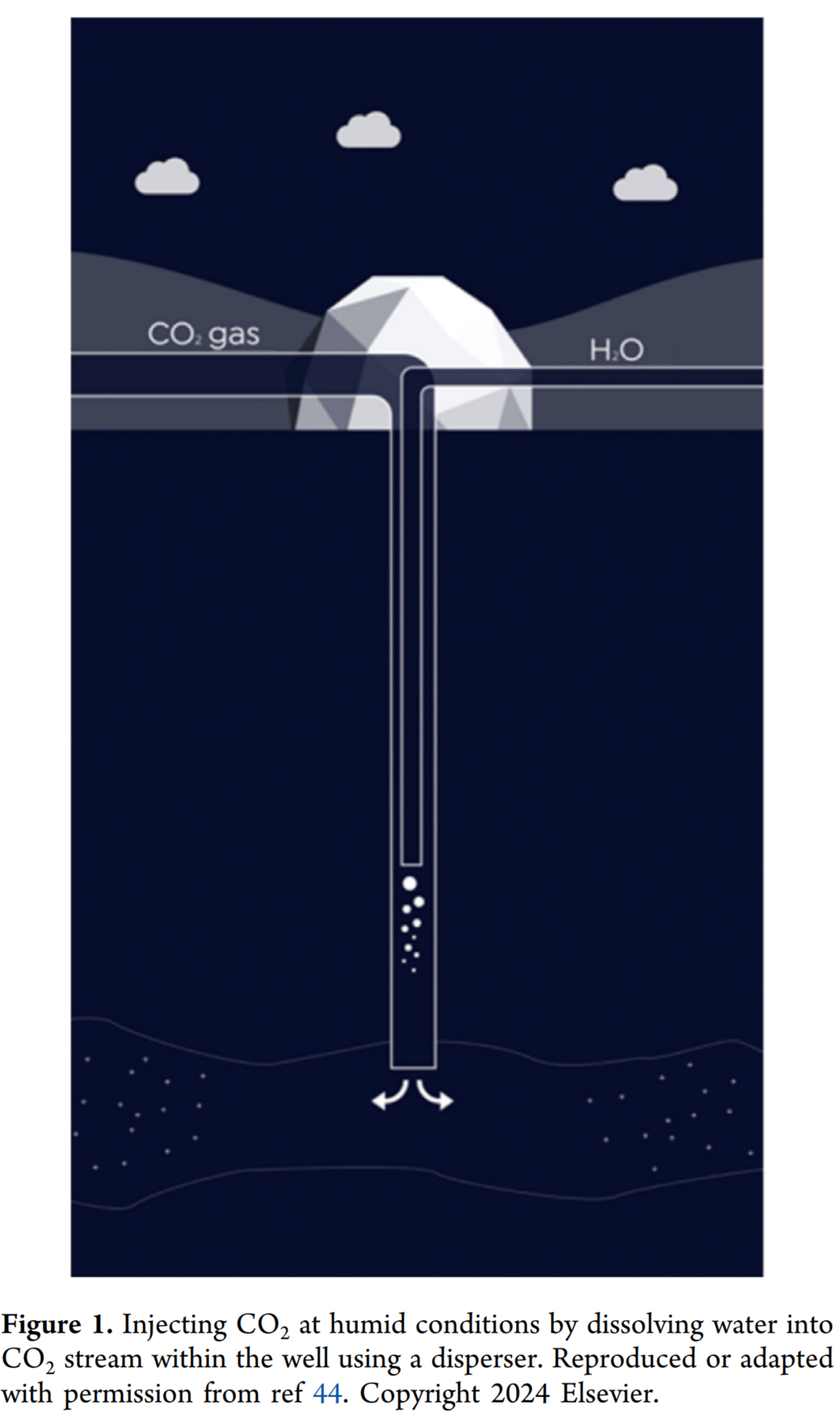
- 提出了两种dwCO₂注入方法:一种是在井内使CO₂饱和水,另一种是在地表使CO₂饱和水。第一种方法可以使CO₂完全饱和水,而第二种方法需要考虑更多的工程因素,以确保在操作过程中CO₂中的水含量保持在安全范围内,避免自由水的形成和相关的腐蚀风险。
- 通过适当的工程设计和管理策略,dwCO₂注入方法可以有效地防止盐析,同时减少与盐析相关的维护成本和基础设施风险。
- 研究强调了在CO₂储存过程中理解和控制水蒸发、盐析以及CO₂捕获机制之间相互作用的重要性,并为优化碳酸盐含水层中的CO₂储存提供了有价值的见解。
作者单位
- 英国赫瑞瓦特大学工程与物理科学学院研究中心(RCCS)
Abstract
CO2 storage in geological formations, particularly deep saline aquifers, is a critical component of carbon capture and storage technology, offering significant potential for mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. However, high salinity of these aquifers poses the risk of salt precipitation, leading to pressurization and injectivity reduction. Developing a method to prevent salt precipitation remains a challenge, and this is an area that this study is focused on. Dissolved-water CO2 injection (dwCO2 injection) is proposed here as a novel method to prevent salt precipitation where water is dissolved in CO2 before injection into an aquifer. Presence of water in the CO2 stream prevents more dissolution of water into CO2 (evaporation) and, hence, prevents salt precipitation. Before presenting this method and in order to provide a good mechanistic understanding of the interactions involved in a CO2 storage process, six different scenarios are examined using the CMG-GEM simulator within a carbonate aquifer. The results showed that saturating CO2 with water reduced the precipitation nearly to zero, and dissolving 2000 ppmv water decreased the salt precipitation to one-third. It should be noted that injection of humid CO2 requires special methods to tackle the potential challenges, including corrosion and hydrate formation risks, and the paper also discusses them.
