A coupled wellbore-reservoir modelling approach to showcase the effect of CO2 injection on flow behavior in a saline aquifer
随着大气中温室气体排放量的增加,碳捕集与封存(CCS)作为一种减少二氧化碳(CO2)排放的解决方案日益受到关注。为了确保CO2在目标储层中长期安全存储,同时避免对井筒和地层完整性造成不利影响,需要对CO2注入过程进行全面研究。本研究采用耦合井筒-储层建模方法,探讨了CO2注入对流动行为的影响,针对两个潜在目标储层:含盐水层和枯竭气田。研究结果展示了不同捕集机制的效率,如结构捕集、残余捕集、溶解捕集和矿物捕集等。此外,研究还计算了Bryne和Sandnes地层以及Frigg枯竭气田的破裂压力,并通过阶梯速率注入测试确定了最优CO2注入率。热模拟结果表明,温度变化对CO2相态行为有显著影响,进而影响存储效率。最终,通过敏感性分析确定了CO2存储的最佳条件。研究结果为优化CCS项目中的CO2注入策略、理解CO2在不同条件下的行为以及确保地质构造的完整性提供了全面框架。
CMG软件应用情况
在本研究中,CMG(Computer Modelling Group)软件被用于模拟CO2在地质构造中的注入和储存过程。CMG软件能够处理复杂的热力学和流体力学问题,提供了多种模拟工具来分析CO2注入量的变化。研究中使用了CMG GEM™模拟器,它是一个组成性和非常规模拟器,广泛用于模拟CO2和H2存储过程。CMG软件的模拟周期包括建立模型、运行模拟和结果可视化,整个过程通过CMG BUILDER™、WINPROP™和RESULTS™等工具完成。
结论
- 本研究通过耦合井筒-储层建模方法,全面分析了CO2注入对流动行为的影响,为CCS项目的优化设计提供了科学依据。
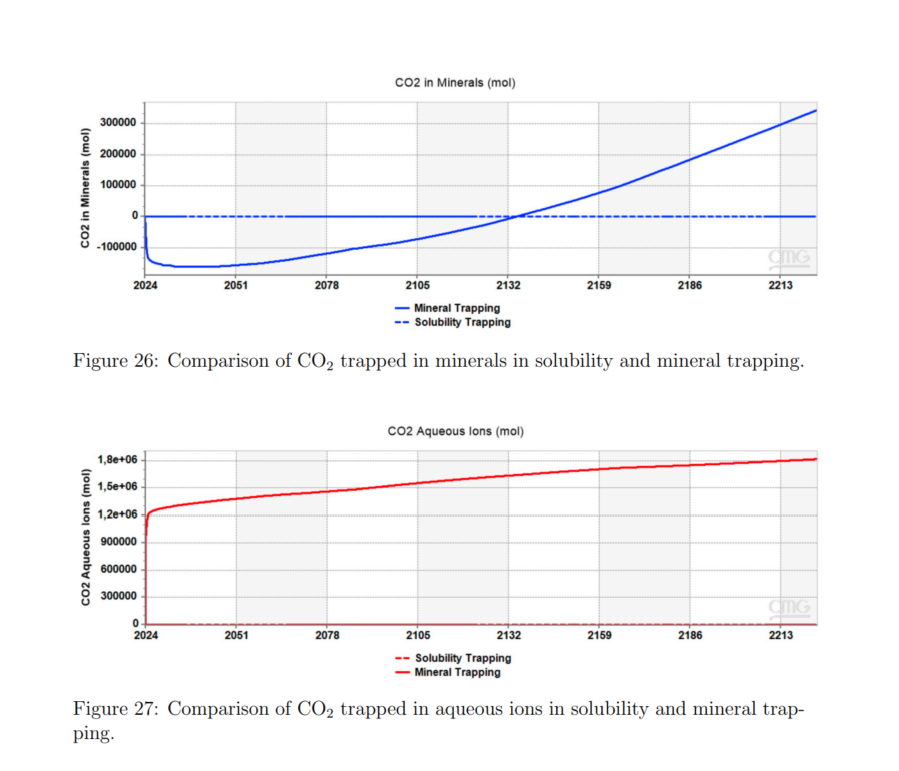
- 研究结果表明,结构捕集、残余捕集、溶解捕集和矿物捕集是CO2存储中的主要机制,其中矿物捕集在200年内可捕获高达5%的注入CO2。
- 计算得到Bryne和Sandnes地层的破裂压力为515 bara,Frigg枯竭气田的破裂压力为150 bara,确保了注入率低于这些值以保证安全。
- 通过阶梯速率注入测试,确定了10,000 m3/day为Bryne和Sandnes地层的最优CO2注入率,平衡了存储效率和地层完整性。
- 热模拟显示温度变化显著影响CO2相态行为,如溶解度、密度和粘度,进而影响存储效率。
- 敏感性分析表明,较低的储层压力、较高的孔隙度和较低的初始水饱和度可使CO2存储容量增加约60%。
作者单位
挪威科技大学工程学院地质科学与石油系

Summary
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is on the rise as a solution for reducing the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere, which is considered the main reason behind global warming. To safely store CO2 in a prospective site, for a long period without causing any adverse e↵ects on the integrity of the wellbore and formation, a comprehensive study should take place to account for all the possible challenges and complications faced during and after injection. This study investigates the e↵ect of CO2 injection on flow behavior, using a coupled wellbore-reservoir modeling approach, considering two targeted sites: a saline aquifer and a depleted gas field. Key findings from the simulation results include the e2 within geological formations, residual trapping caused 40% of CO2 to be immobilized in deeper pore spaces, solubility trapping enhanced the retention of CO2 by significantly increasing CO2 mole fractions in water, and mineral trapping showed e2 over a span of 200 years. In addition, fracture pressure for Bryne and Sandnes formations was calculated using Eaton’s method at 515 bara, ensuring safe injection rates below this constraint, similarly for the Frigg depleted field where the fracture pressure was calculated at 150 bara. Step-rate injection test was done to identify the optimal rate of CO2 injection of 10,000 m3/day, balancing both storage e2 phase behavior. This a↵ects for example the solubility of CO2 in brine, the geochemical reactions, the density and viscosity of both CO2 and brine, and the porosity of the formation. Phase diagrams were generated to examine the phase changes of CO2 under di↵erent conditions to better understand their e↵ect on storage e2 storage. It indicated that lower reservoir pressure, higher porosity, and lower initial water saturation increased the storage capacity by around 60%. This study o↵ers a comprehensive framework for optimizing CO2 injection strategies in CCS projects, understanding how CO2 is behaving under di↵erent conditions, and ensuring the integrity of geological formations.
Keywords:
CO2 injection, coupling approach, thermal e↵ects.
