Numerical simulation study on enhanced efficiency of carbon dioxide geological storage with nanoparticles in deep saline aquifer
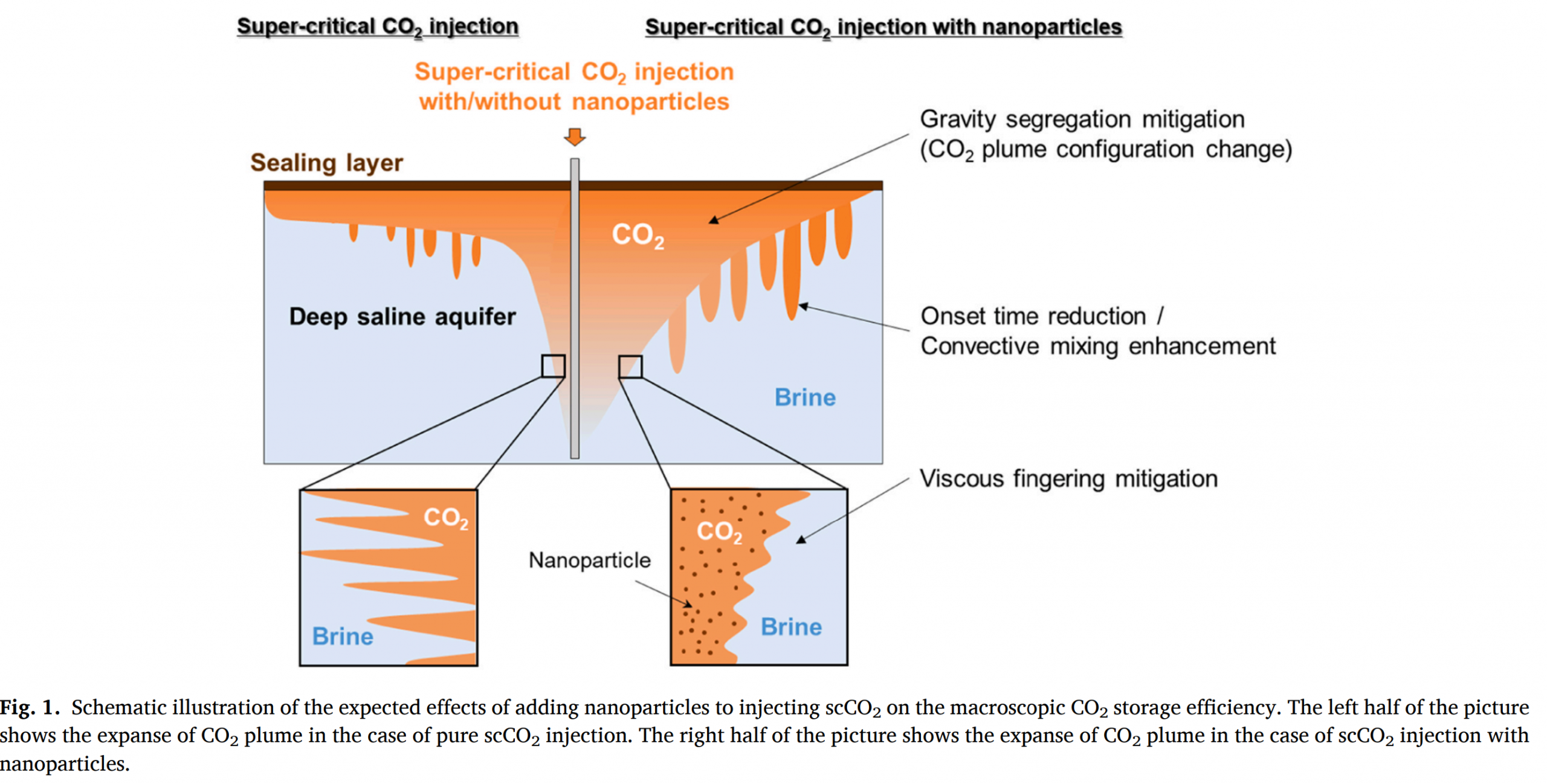
深部咸水含水层因其在所有可能的CO2地下储存地点中拥有最大的潜力而受到极大关注。注入深部咸水层的CO2会因浮力作用向上迁移,直到达到封闭层,这导致了储存效率不高。近年来,一些新研究发表了利用纳米颗粒进行CO2地质储存的方法。向注入的超临界CO2(scCO2)中添加纳米颗粒会改变其物理性质,如密度和粘度,这可能减轻重力分离和粘性指进现象。然而,与这些技术相关的研究仍然极为有限,其潜在优势或影响尚不清楚。
本文中,我们使用多功能商业模拟器(CMG-GEM)研究了含有纳米颗粒的scCO2的物理性质对储存效率的影响,特别是纳米颗粒类型(氧化铝、二氧化硅、二氧化钛和氧化锌)和浓度对CO2储存效率的影响,通过考虑可能的运行场景进行了定量展示。
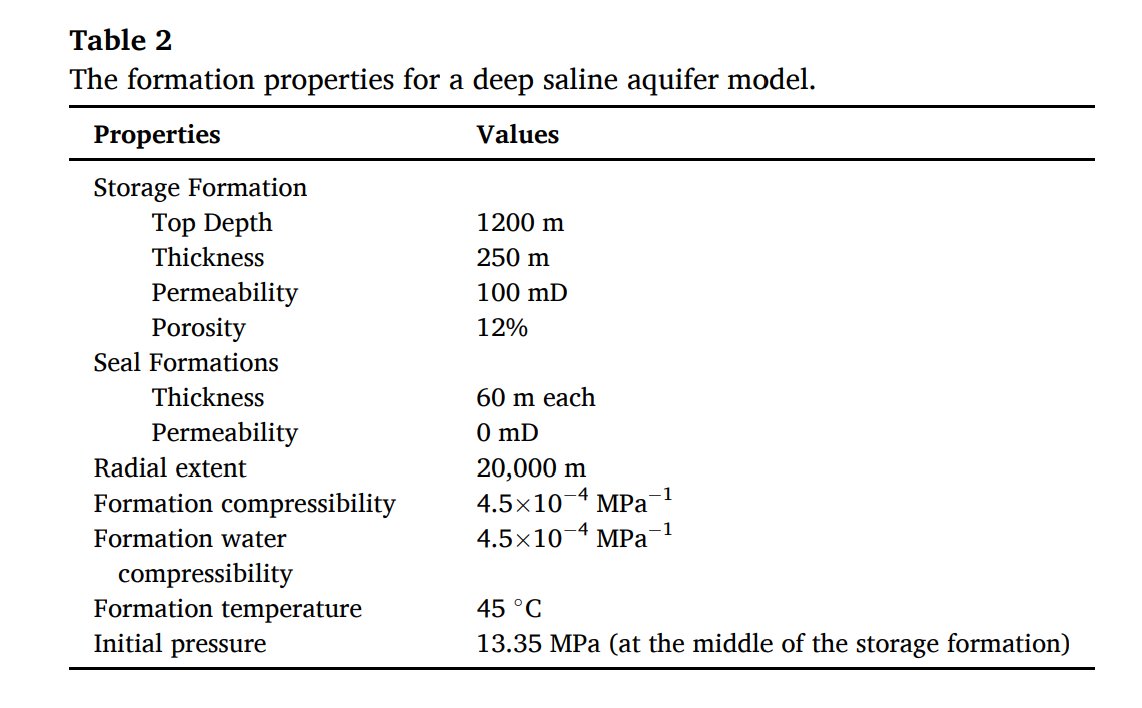
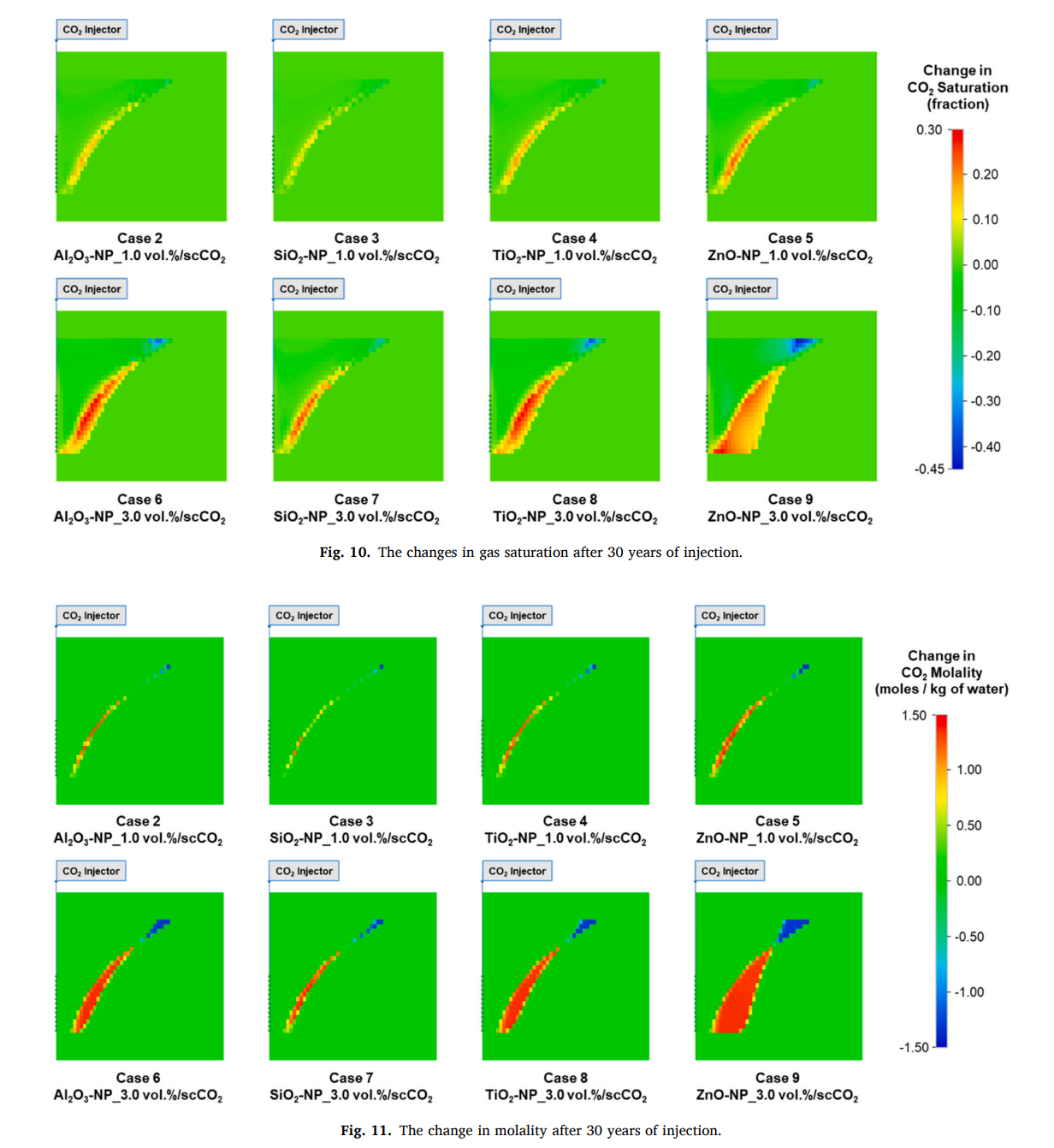
结果表明,当scCO2与纳米颗粒一起注入时,CO2向含水层上部的迁移被抑制,而CO2在含水层下部的储存得到促进。在假设压力控制井的情况下,还展示了延迟突破时间和减轻突破量的一些效果。结果表明,在30年后,累积突破量在最小情况下减少了8.2%,在最大情况下减少了79.3%。尽管提出的方法仍面临经济挑战,但纳米颗粒生产过程的创新或与附加值的结合将提高可行性。
CMG软件应用情况
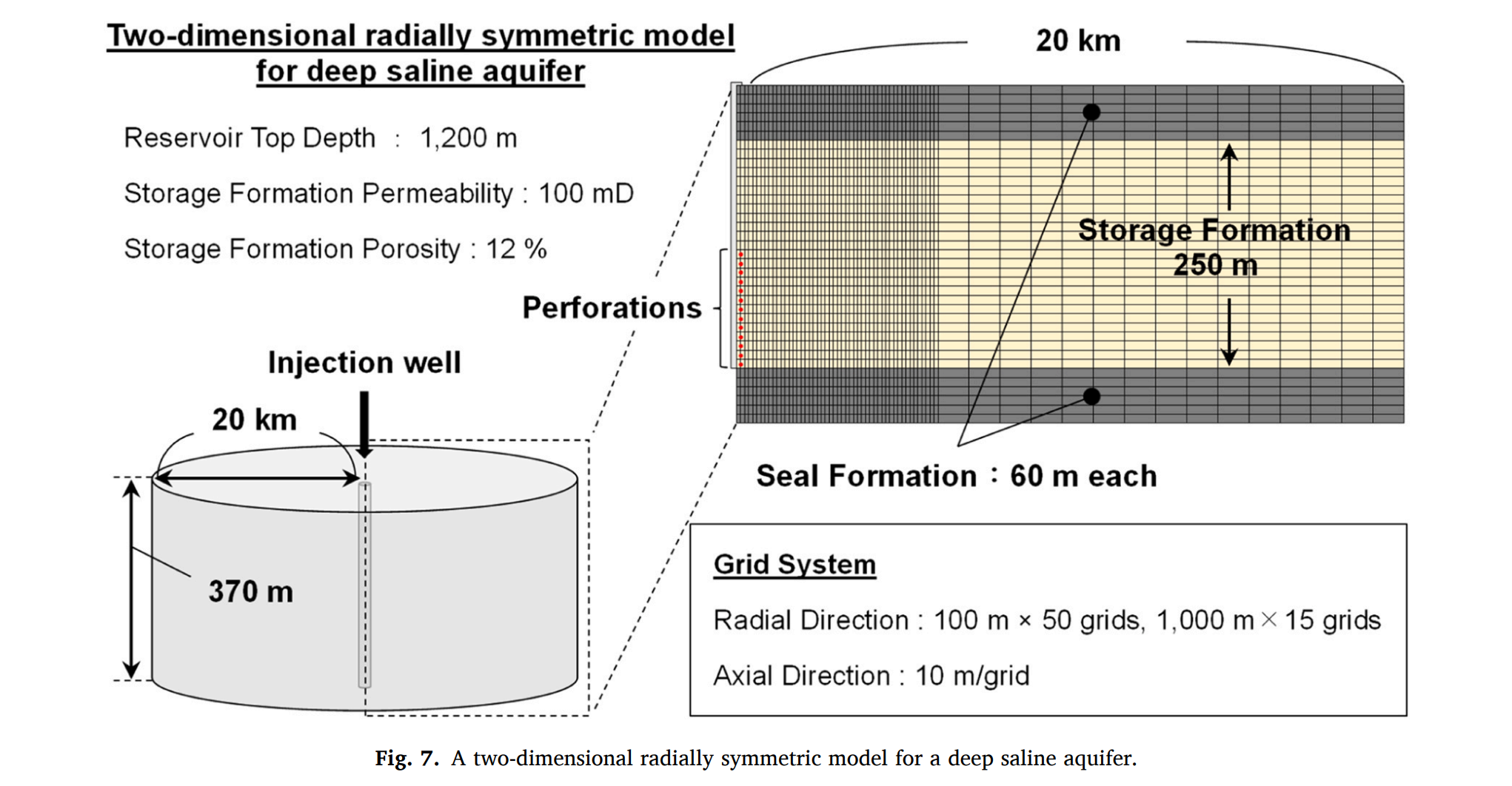
在本研究中,使用了CMG-GEM商业组分储层模拟器来模拟深部咸水层中的CO2地下储存。CMG-GEM带有常见的方程状态(EoS)模型,如PR和SRK模型。由于Span和Wagner EoS能够准确拟合许多关于CO2密度测量的文献值,因此调整了PR EoS的体积位移参数以拟合Span和Wagner EoS计算的CO2密度。使用了CMG的流体建模软件CMG-WinProp生成EoS模型。为NP/scCO2的流体模型创建了四种金属氧化物纳米颗粒不同浓度(1.0体积%和3.0体积%)的一些拟流体模型。
Abstract
Geological storage of carbon dioxide (CO2) is a promising technique to reduce large-scale greenhouse gas emissions. There are some candidates for geological storage formation while deep saline aquifers have attracted tremendous attention because they have the largest potential of all possible subsurface storage sites. CO2 injected into deep saline aquifers migrates upward until it reaches a sealing formation due to its buoyancy effect, which causes poor storage efficiency. Over the past few years, some novel research has been published to utilize nanoparticles for CO2 geological storage. The addition of nanoparticles to injecting super-critical CO2 (scCO2) changes its physical properties, such as the density and viscosity, which could mitigate gravity segregation and viscous fingering. However, the studies related to these techniques are still extremely limited, and the potential advantages or their impacts are poorly understood. In this paper, we investigated the effects of the physical properties of scCO2 containing nanoparticles on storage efficiency by using a versatile commercial simulator (CMG-GEM). In particular, the effects of nanoparticle types (aluminum oxide, silicon dioxide, titanium oxide, and zinc oxide) and concentration on CO2 storage efficiency were presented quantitatively by considering possible operation scenarios. The results showed the migration of CO2 to the upper part of the aquifer was suppressed, and the storage of CO2 in the lower part of the aquifer was promoted when scCO2 was injected with nanoparticles. It also showed some effects in delaying breakthrough time and mitigating breakthrough amount when we assumed the pressure control well. It was indicated that the cumulative breakthrough amount after 30 years was reduced by 8.2% in the minimum case and by 79.3% in the maximum case. Although the proposed method still has economic challenges, the innovation in the production processes of nanoparticles or combining with added value will lead to improving feasibility.
作者单位:
日本国际碳中和能源研究所,熊本大学
