Simulation-Based Optimization Workflow of CO2-EOR for Hydraulic Fractured Wells in Wolfcamp a Formation
本研究针对美国德克萨斯州二叠纪盆地Wolfcamp A地层的非常规油藏,通过耦合地质力学-油藏模拟技术,优化了多级压裂水平井的二氧化碳吞吐(CO2 Huff-n-Puff)过程,研究同时考虑了提高石油采收率和CO2封存的潜力。
利用1D地质力学模型得出的地质力学属性参数,集成到油藏模拟中,以再现水力裂缝的几何形态。通过大量的生产历史拟合验证了裂缝模型。流体相态行为分析优化了状态方程,1D细管模拟确定了CO2注入的最小混相压力为4300 psi。
在主要生产阶段后,测试了从1到25 MMSCFD/井的不同CO2注入速度,结果表明,增加的石油采收率从6.3%到69.3%不等。分析了不同的注入、焖井和生产周期,以确定最优的操作条件。最优方案在保持最高的CO2储存效率的同时,提高了68.8%的累积采收率。本研究提出的模拟方法为评估和优化水力压裂井中的二氧化碳吞吐提供了系统的工作流程,提高了非常规油藏的采收率。
CMG软件的应用情况:
在本研究中,CMG-GEM软件被用于进行1D细管模拟以估计最小混相压力(MMP),以及网格到网格的模拟,以更好地理解CO2与储层油之间的混相行为。此外,CMG-GEM软件还用于模拟周期CO2注入,以验证CO2 Huff-n-Puff过程的效率。
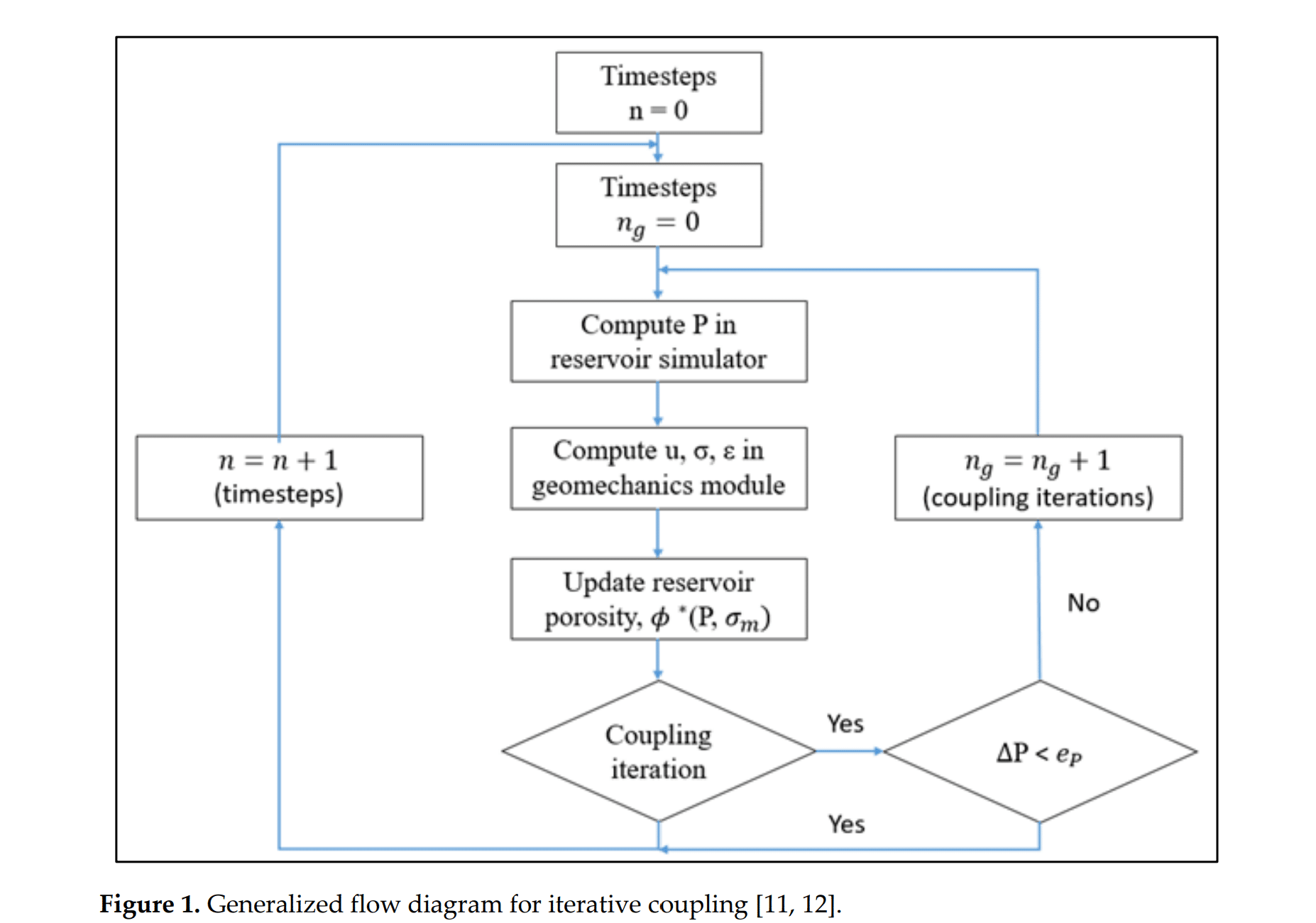
图 1. 迭代耦合流程的通用流程图
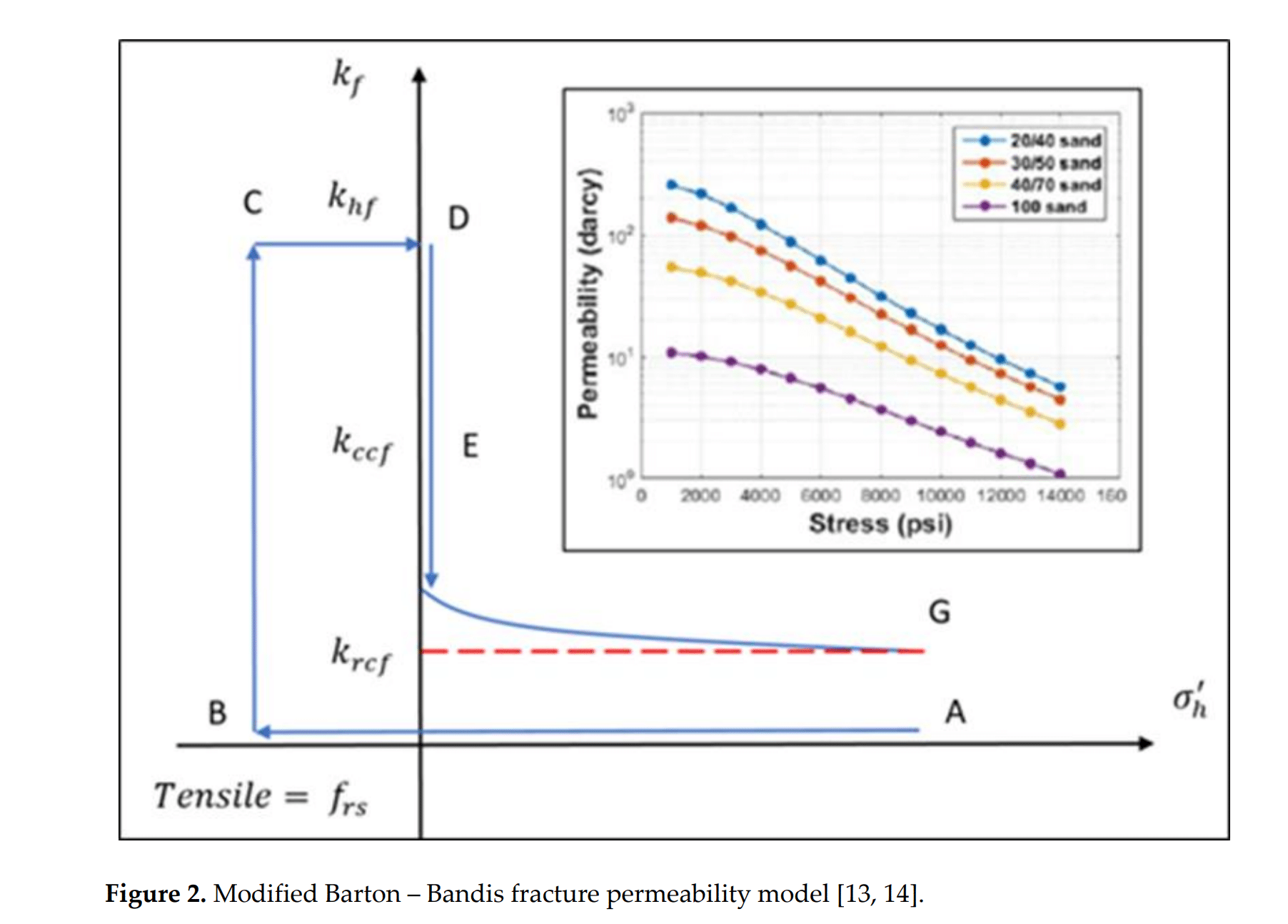
图2修公的 Barton-Bandis 裂缝渗透率模型
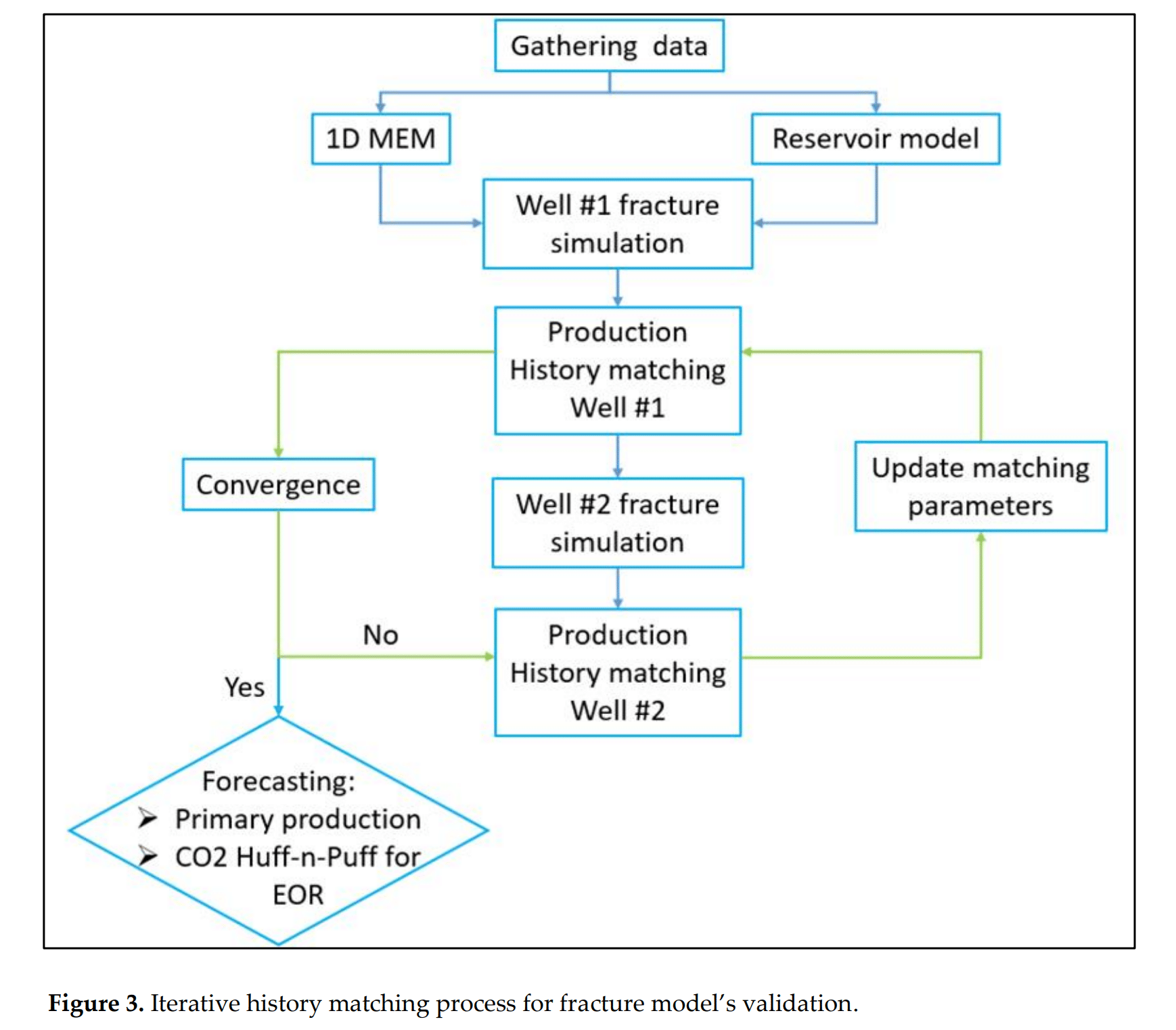
图 3. 迭代历史拟合过程,用于裂缝模型的验证
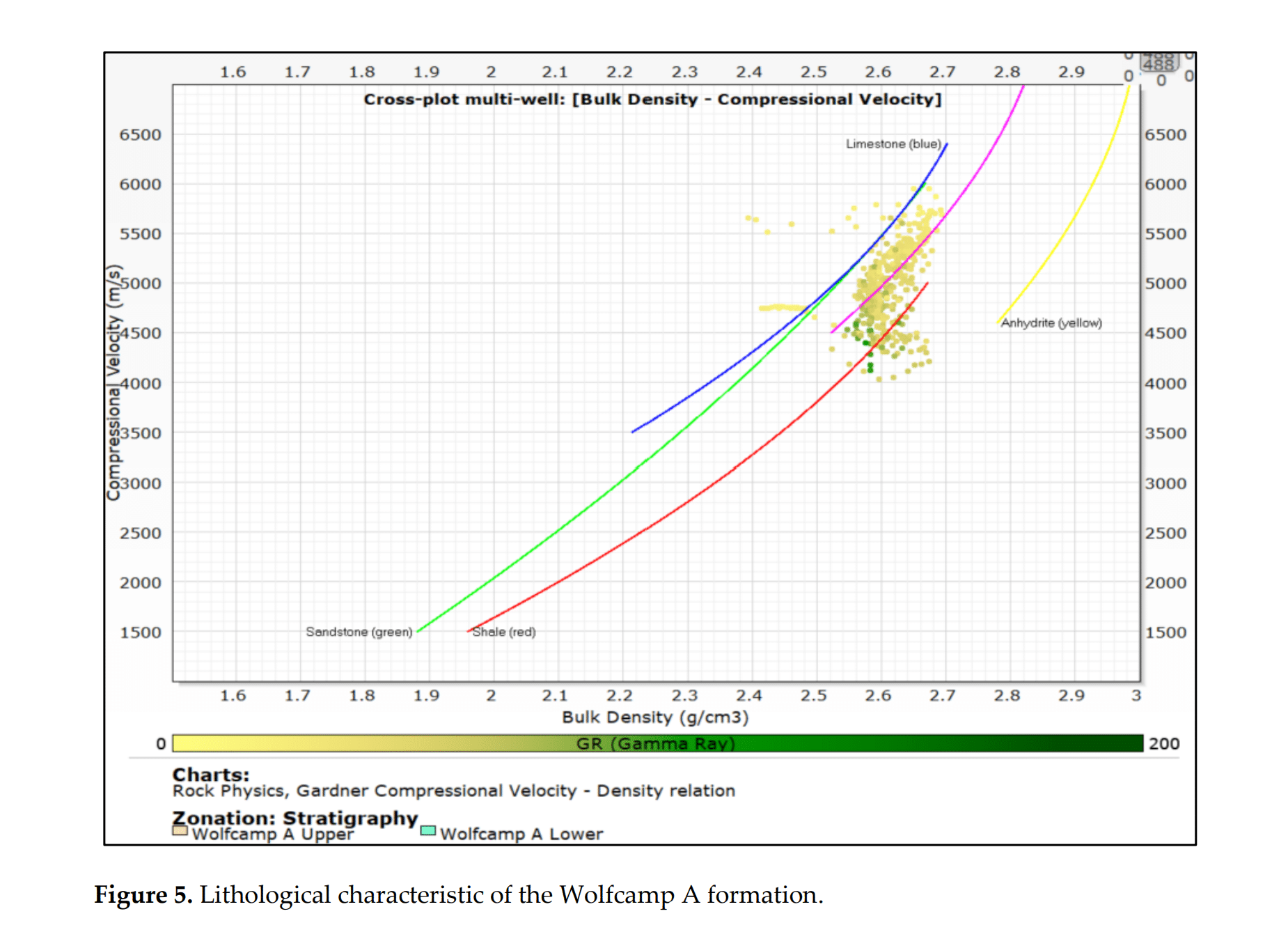
图 5. Wolfcamp A 地层的岩性特征

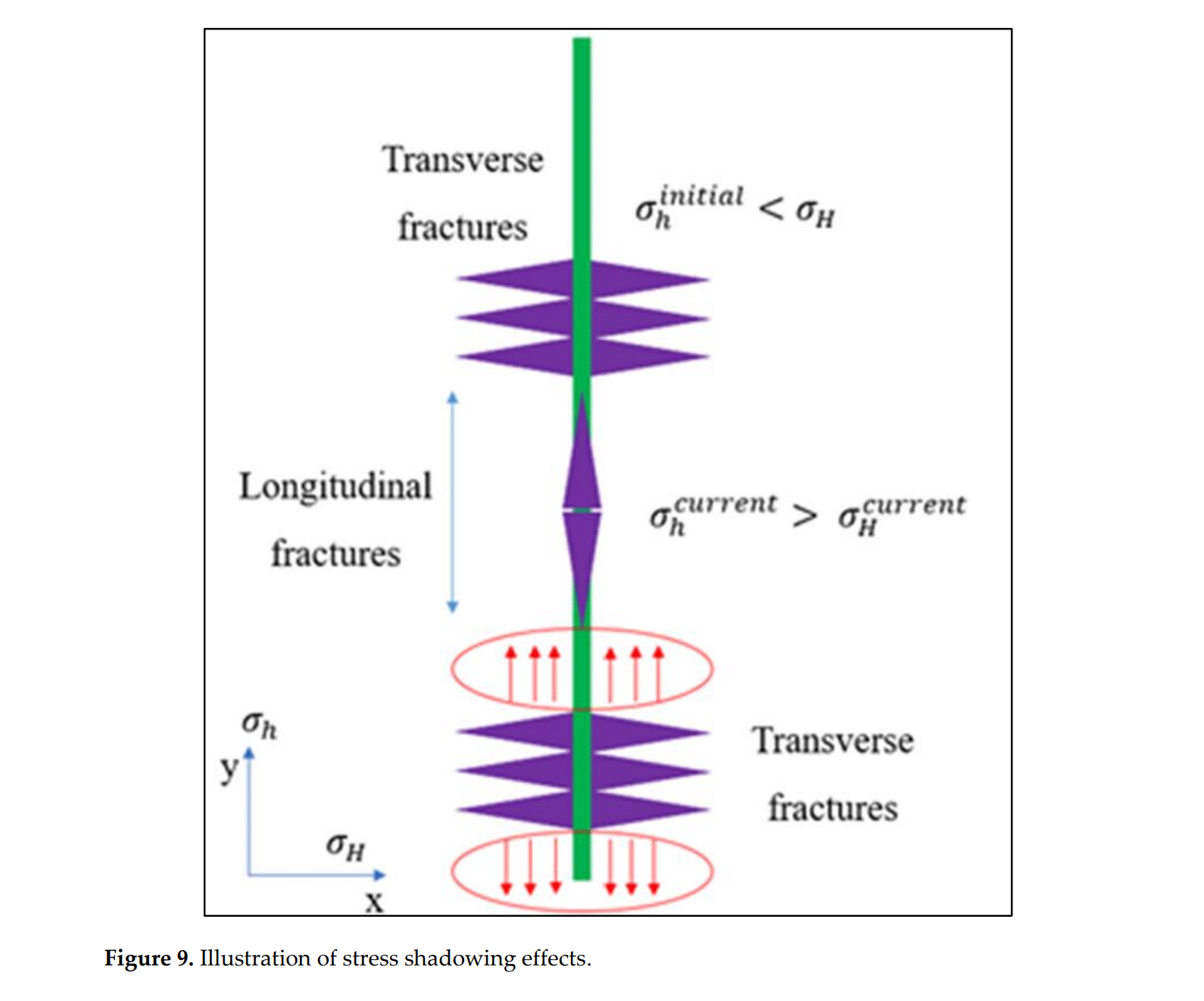
图 9. 应力阴影效应的示意图
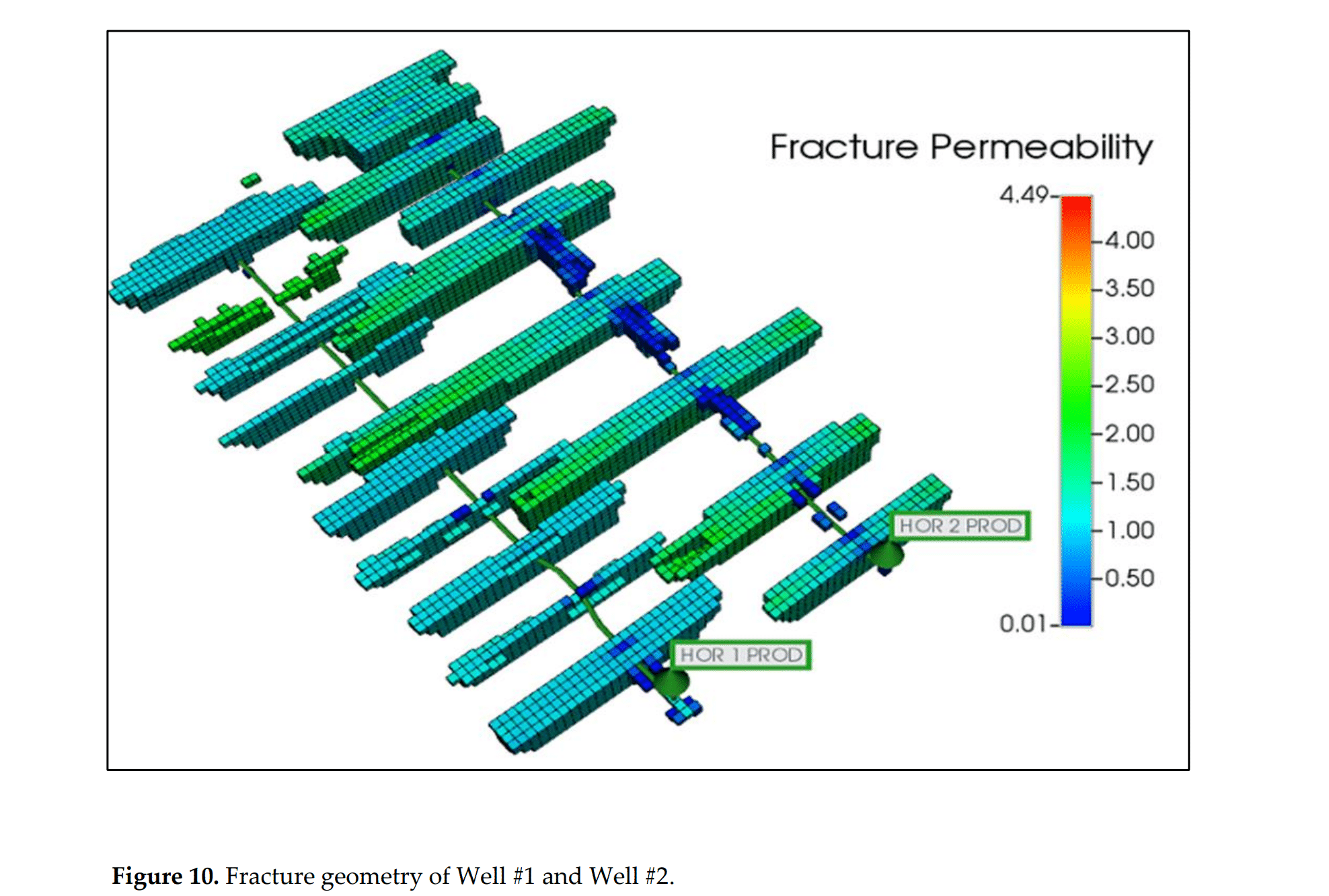
图 10. #1 井和#2井 的裂缝几何形态
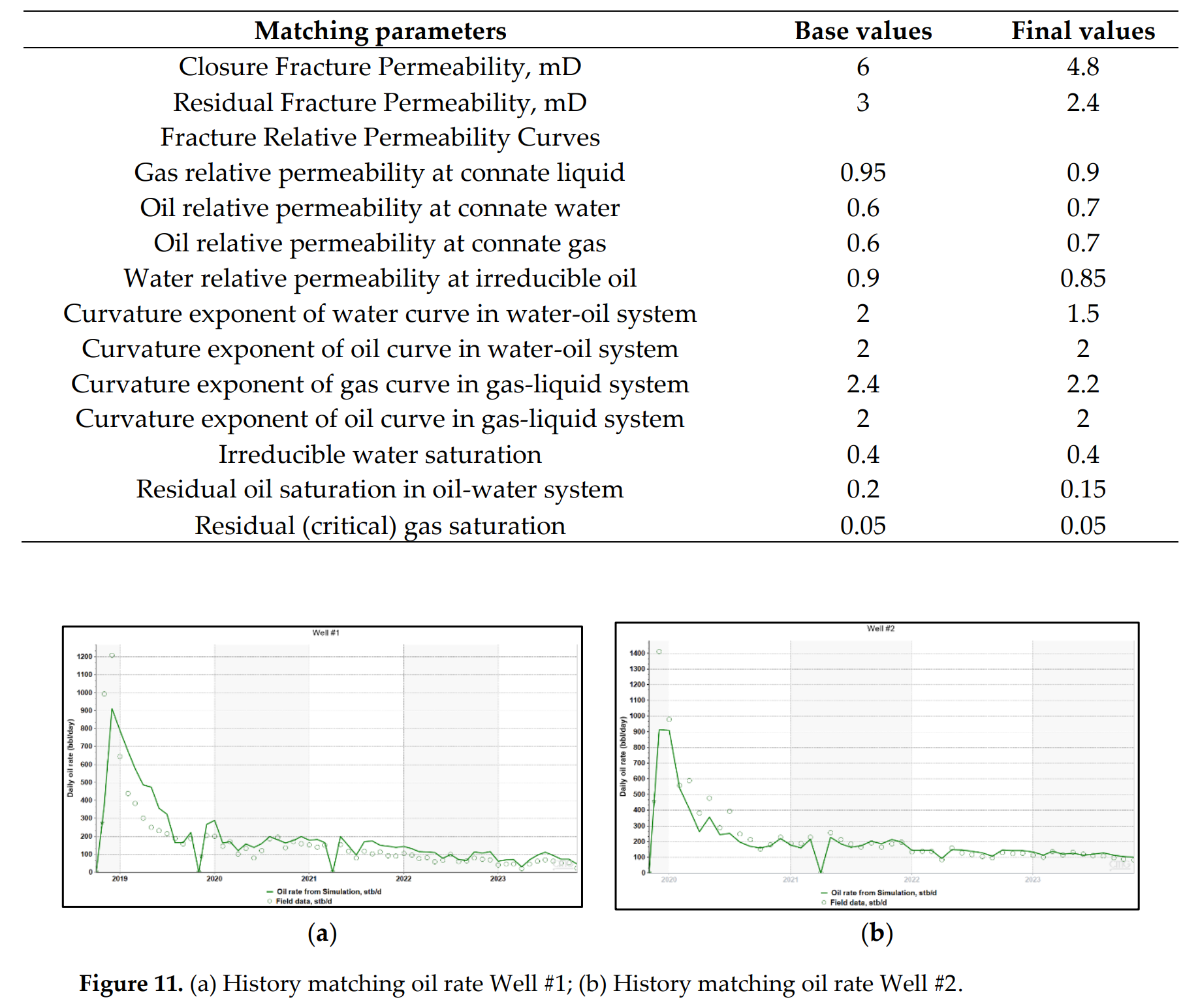
图 11. (a) #1井产油历史拟合;(b) #2井产油历史拟合
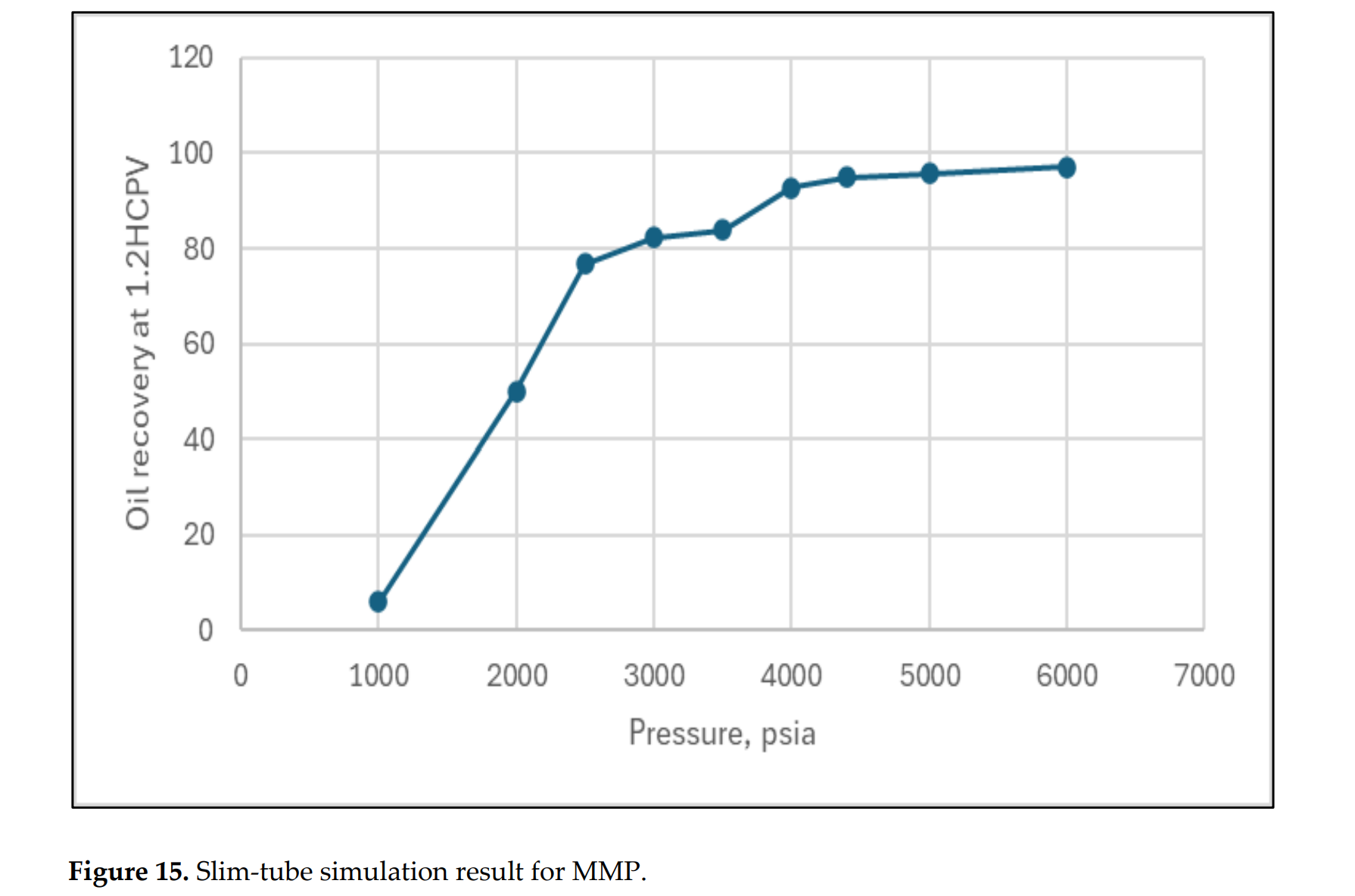
图15 MMP的细管模拟结果
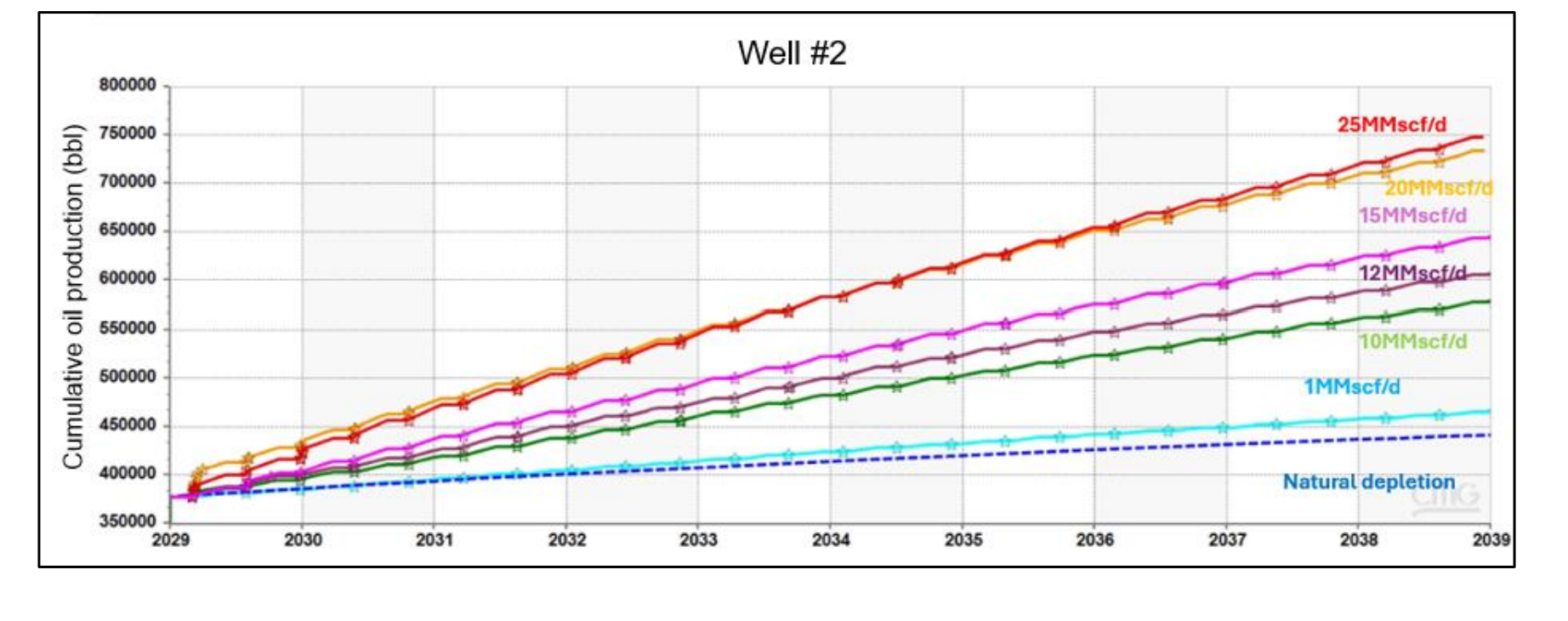 图 19. 不同 CO2 注入速度下的 累计产油量
图 19. 不同 CO2 注入速度下的 累计产油量
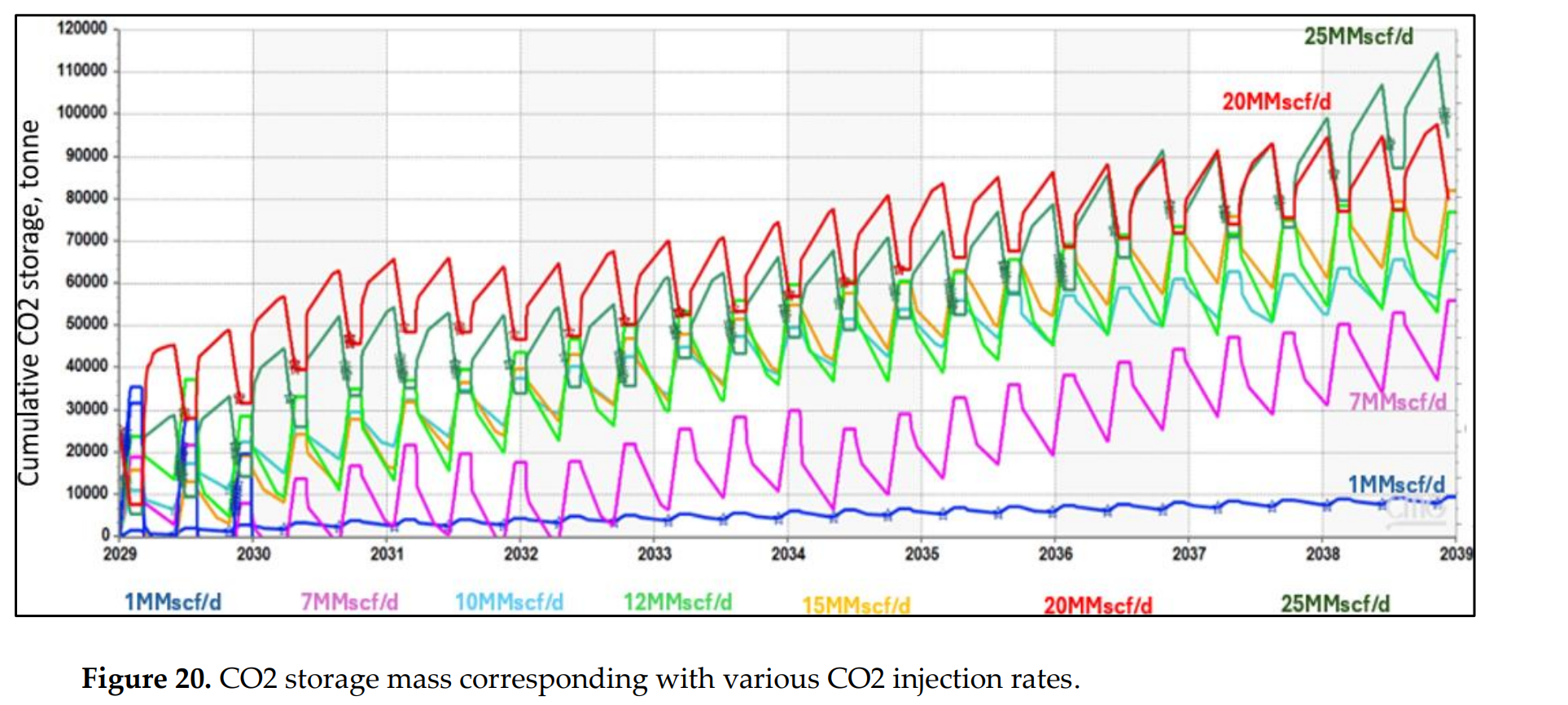
图 20. 不同 CO2 注入速度下的 CO2 储存量
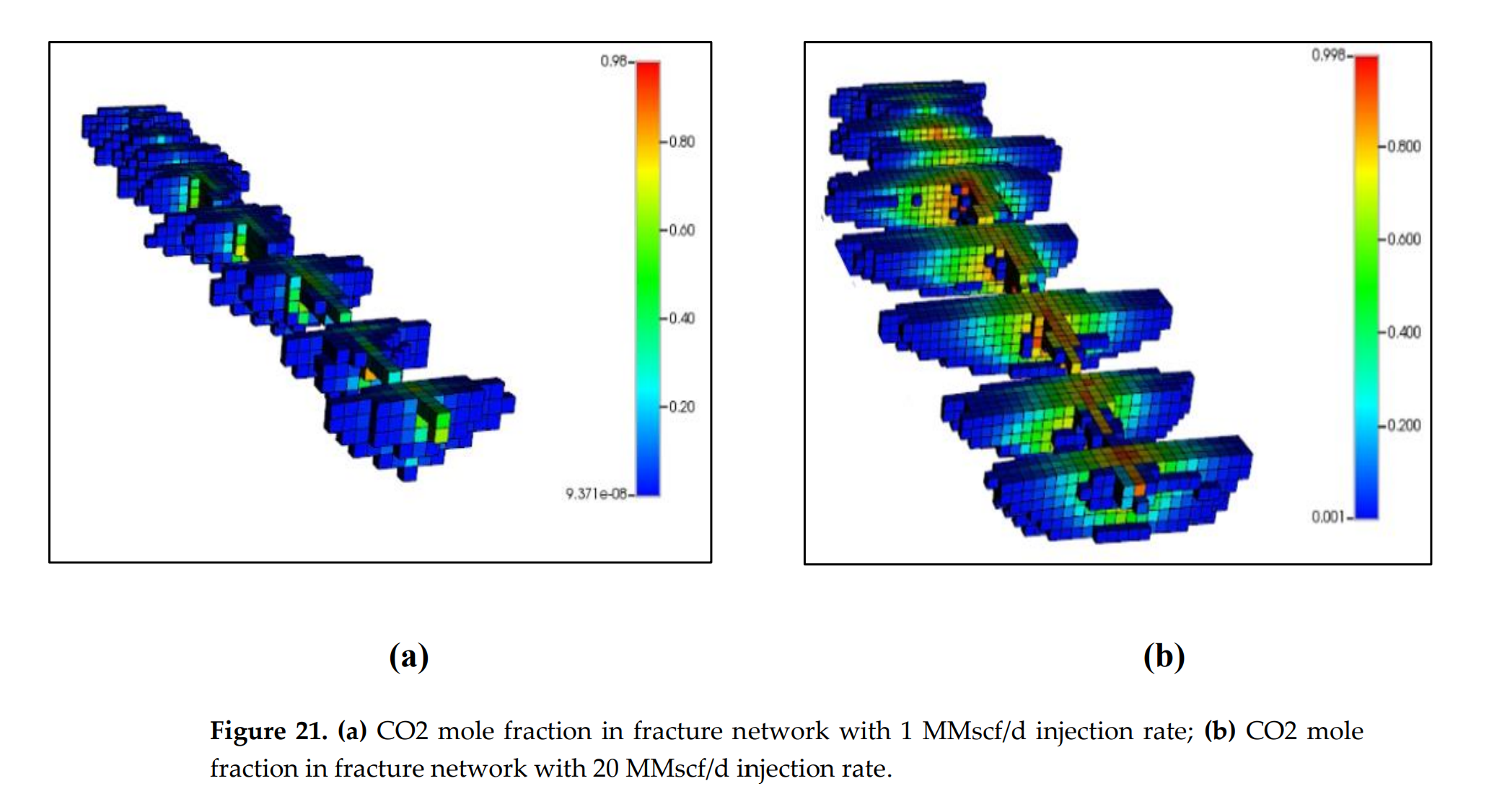
图 21. (a) 1 MMscf/d 注入速度下裂缝网络中的 CO2 摩尔分数;(b) 20 MMscf/d 注入速度下裂缝网络中的 CO2 摩尔分数
中文单位:
- 新墨西哥矿业理工学院(New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology)
- 休斯顿大学(University of Houston)
- 北卡罗来纳大学彭布罗克分校(The University of North Carolina at Pembroke)
Abstract:
Hydraulic fracturing has enabled production from unconventional reservoirs in the U.S., but production rates often decline sharply, limiting recovery factors to under 10%. This study optimizes the CO2 huff-n-puff process for multistage-fractured horizontal wells in Wolfcamp A formation in the Delaware Basin. The potential for enhanced oil recovery and CO2 sequestration simultaneously was addressed using a coupled geomechanics-reservoir simulation. Geomechanical properties were derived from a 1D mechanical earth model and integrated into reservoir simulation to replicate hydraulic fracture geometries. The fracture model was validated using a robust production history matching. Fluid phase behavior analysis refined the equation of state, and 1D slim tube simulations determined a minimum miscibility pressure of 4300 psi for CO2 injection. After the primary production phase, various CO2 injection rates were tested from 1 to 25 MMSCFD/well, resulting in incremental oil recovery ranging from 6.3% to 69.3%. Different injection, soaking, and production cycles were analyzed to determine the ideal operating condition. The optimal scenario improved cumulative oil recovery by 68.8% while keeping the highest CO2 storage efficiency. The simulation approach proposed by this study provides a systematic workflow for evaluating and optimizing CO2 huff-n-puff in hydraulically fractured wells, enhancing the recovery factor of unconventional reservoirs.
Keywords:
CO2-EOR Huff-n-Puff; Hydraulic fracturing simulation; Hydrodynamic-geomechanical coupled model; Wolfcamp A formation; Optimizing recovery of unconventional reservoir
